Beyond LSDs: How LRTs and Mitosis Unlock Efficient Cross-Chain Yield

Introduction
Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs) like stETH and mSOL brought staking yields to DeFi, but they’re no longer enough. In 2025, we’re seeing the rise of Liquidity Routing Tokens (LRTs)—yield-bearing assets dynamically routed across multiple strategies. This evolution aligns with the broader shift to modular execution and intent-based DeFi, where projects like Mitosis abstract away the complexity of yield optimization and asset movement.
In this article, we explore how LRTs extend the LSD model, how they’re being integrated into cross-chain systems, and how Mitosis enables intent-based yield abstraction through its modular architecture.
What Are LRTs?
Liquidity Routing Tokens (LRTs) are assets that represent stake in multiple composable yield strategies—re-staking, lending, farming, and more. Unlike traditional LSDs, which wrap a staking position on one network, LRTs:
- Enable cross-strategy liquidity
- Support re-staking on platforms like EigenLayer
- Interact with protocols like Pendle for yield trading
Examples include:
- eETH (EtherFi): re-staked ETH
- rsETH (Renzo): LST + EigenLayer points
- nETH (KelpDAO): optimized for EigenLayer AVS rewards
These LRTs reflect not just staking rewards, but composite DeFi strategies, creating demand for routing systems that can handle them.
LSD → LRT → Mitosis: Intent-Based Yield Routing
Mitosis integrates LRTs into its intent-based execution layer, using its internal architecture to turn user deposits into composable, yield-seeking capital.
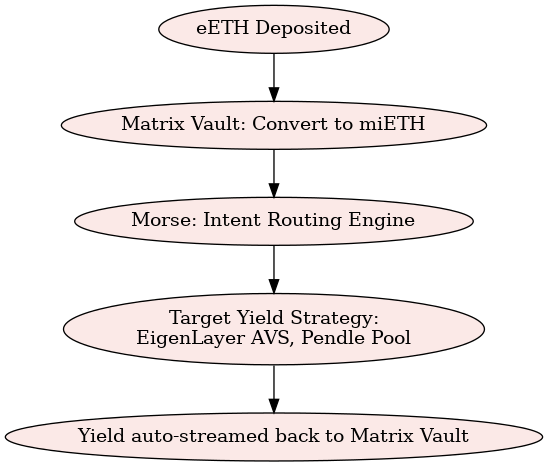
Key Components:
- Matrix Vaults: Accept LRTs like eETH and issue wrapped miAssets
- Morse: Executes intents across chains and strategies
- Yield Strategies: Accesses AVSs, Pendle pools, or future Mitosis-native strategies
Through intent submission, a user requests “optimal yield on eETH”—and Mitosis handles the rest.
Yield Abstraction in Practice
LRTs are powerful, but they’re still hard to manage manually:
- Where to re-stake?
- When to rotate strategies?
- How to bridge capital?
Mitosis abstracts this. It becomes the modular infrastructure layer that lets users deposit once and benefit from:
- Solver-optimized strategy routing
- Gasless cross-chain execution
- Composability with RWA or LRT pools
This makes Mitosis not just a liquidity router—but a yield abstraction engine for the modular DeFi stack.
LSD vs LRT vs Mitosis Execution Layer
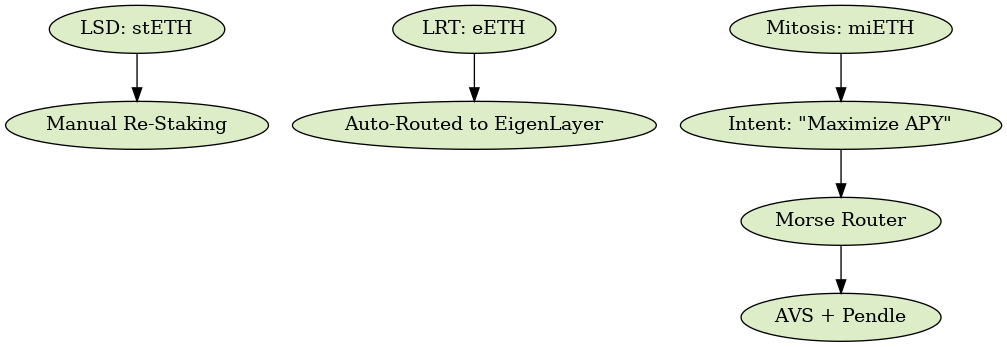
And in table form:
| Property | LSD | LRT | Mitosis Layer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asset Exposure | 1 Chain | Multi-layer yield | Cross-chain abstraction |
| Execution | Manual | Semi-automated | Intent-based + Morse |
| Token Model | stETH, mSOL | eETH, rsETH | miETH, miUSDC |
| UX | Wallet-heavy | Smart LP positions | 1-intent yield automation |
Conclusion
LRTs represent the natural next step in the evolution of DeFi staking—composable, cross-strategy, yield-optimized tokens. But without robust infrastructure, their benefits remain siloed and complex.
Mitosis delivers the missing layer: a modular, intent-based routing protocol that turns user deposits into multi-chain, solver-optimized liquidity. Together, LRTs and Mitosis make automated, yield-maximized DeFi not just possible—but accessible.
References
- Mitosis (2025). Intent-Based Execution in Mitosis
- EigenLayer (2024). Restaking Architecture
- Pendle Finance (2024). LRT Tokenomics and Yield Markets
- Mitosis Glossary: Matrix Vaults, Morse, Vanilla Assets
- Messari (2024). The Liquid Staking Landscape


Comments ()