CEX vs DEX: Which One is Truly Safer and More Practical?

One of the first questions that arises when someone steps into the crypto world is:
"Should I use a centralized exchange or a decentralized one?"
To answer this clearly, it's essential to understand both sides in depth. Let’s explore them with simple yet insightful examples.
What is a CEX? (Centralized Exchange)
A CEX is a trading platform managed by a company or organization. All operations order books, wallets, user data are controlled by this central entity.
A Simple Analogy:
Imagine you're at an airport and you exchange currency at a bureau. The exchange rate, transaction process, and security are all under that bureau's control. A CEX works similarly—you buy and sell crypto within a system offered and managed by someone else.
Advantages of CEX:
- Fast transactions and high liquidity
- User-friendly interface
- Advanced features such as spot and futures trading
Disadvantages of CEX:
- You don’t control your assets directly
- Risk of security breaches (as seen in historical cases)
- May require identity verification (KYC)
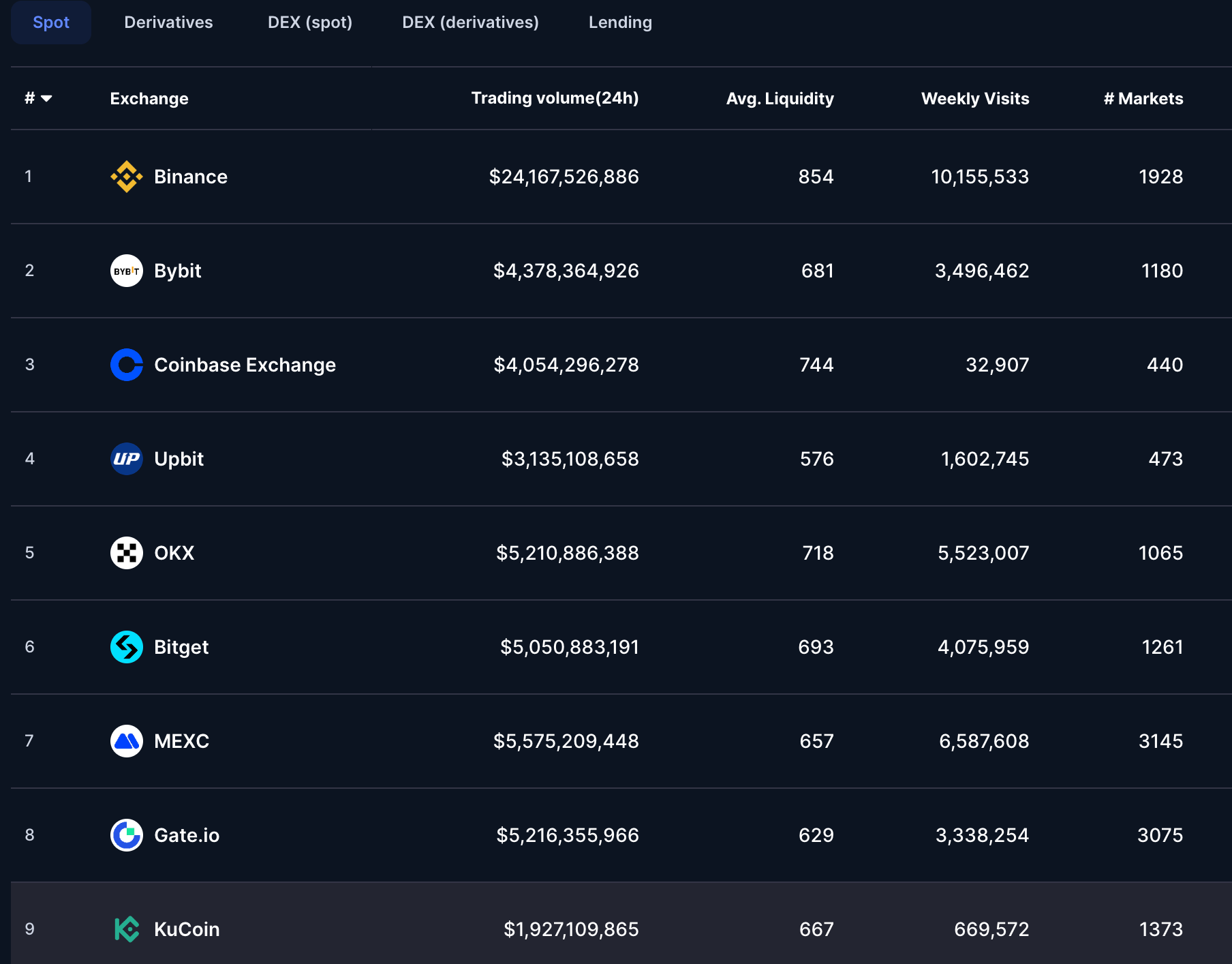
What is a DEX? (Decentralized Exchange)
A DEX allows peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. Transactions are executed directly on the blockchain via smart contracts.
Another Analogy:
You have a wallet at home with your private keys. You take it to a market where each vendor sells their goods directly. You can buy apples or trade for pears—no intermediaries, no middlemen. That’s what a DEX does: direct control and interaction.
Advantages of DEX:
- You control your wallet and funds
- No need to trust a third party
- Enables anonymous transactions
Disadvantages of DEX:
- May require technical knowledge to use
- Network congestion can slow transactions
- Risks associated with smart contract vulnerabilities if unaudited
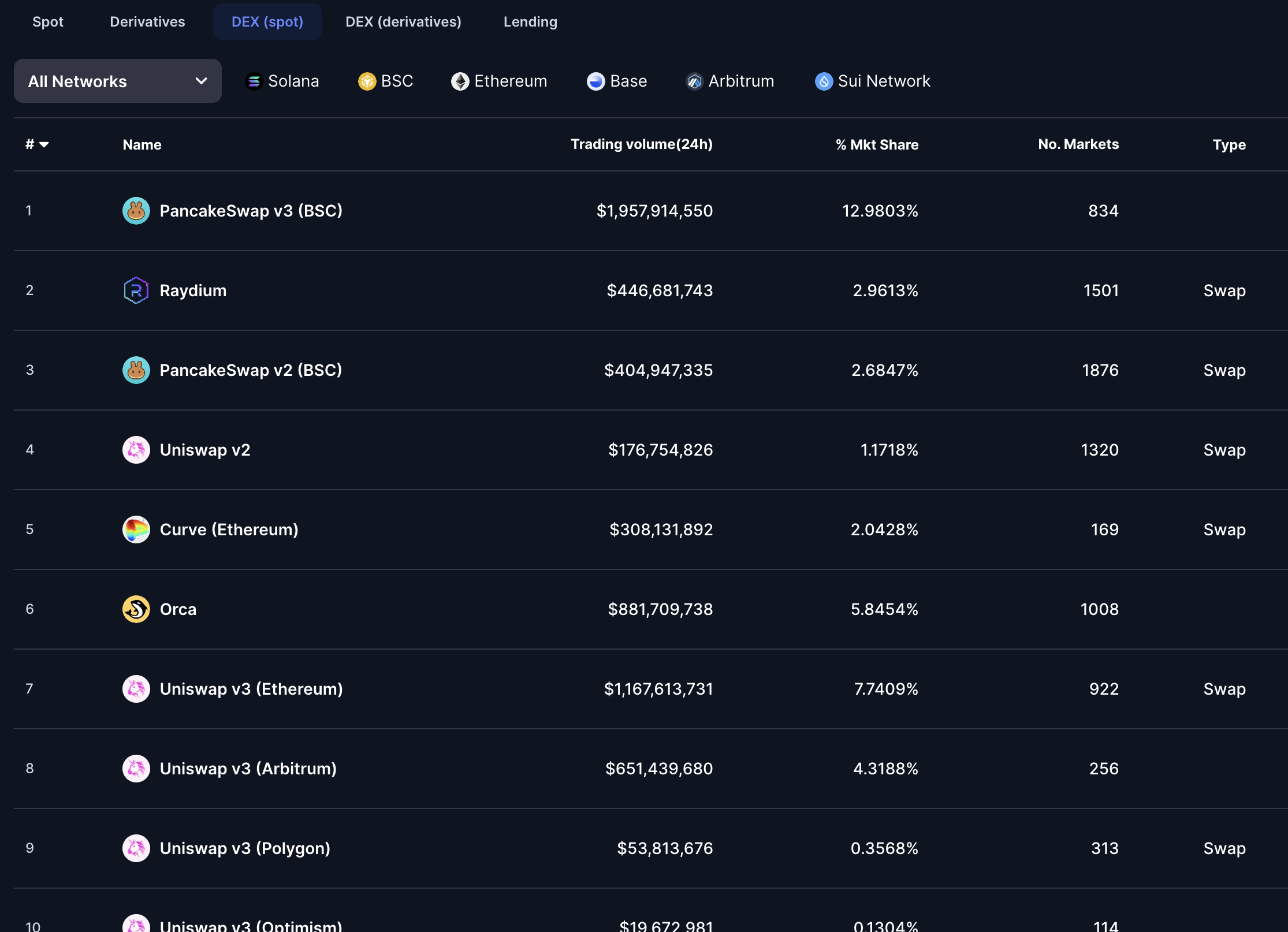
Let’s Break It Down with Examples
1. Asset Control
CEX: Your private keys are held by the exchange. You entrust your funds to the platform.
DEX: You hold your own keys. Full self-custody.
Think about it: It’s like parking your car at a valet (CEX) versus keeping your keys in your pocket and parking yourself (DEX).
2. Order Types and Speed
CEX: Offers limit, stop-limit, margin, and leveraged trading.
DEX: Usually provides simple swap mechanisms; no order book.
Think about it: A CEX is like a fine-dining restaurant with a complex menu. A DEX is more like a buffet—quick, straightforward, and flexible.
3. Privacy and Anonymity
CEX: May require KYC and keep transaction records.
DEX: Only interacts with your wallet address; no personal ID is required.
Think about it: One asks for your ID, the other just interacts with your wallet—clear difference in privacy.
Security: Which One is Safer?
This is a frequently asked, but situational, question.
CEX: Being centralized, a hack can affect all users if the platform is compromised.
DEX: No central point of failure, but vulnerable to poorly written smart contracts or user error in wallet security.
In summary:
- CEX says: “Trust us.”
- DEX says: “Trust only yourself.”
Which Exchange Type Suits Whom?
| User Type | Preference Reason | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Simple interface | ✅ CEX |
| Experienced User | Full control over assets | ✅ DEX |
| High-Frequency Trader | Fast order matching | ✅ CEX |
| Privacy-Conscious Trader | Anonymous trading | ✅ DEX |
| Web3 Enthusiast | Contributing to networks via gas fees | ✅ DEX |
Final Thoughts: Both Have Their Place
CEXs are ideal gateways for beginners and those who value convenience.
DEXs are essential for those who value privacy, control, and align with the Web3 philosophy.
The smartest strategy is to know both ecosystems and understand when each is more appropriate. After all, that’s the spirit of Web3: awareness, choice, and control


Comments ()