🧠 Cross-Chain Data Availability: The Key to Scalable and Secure Modular Blockchains

Category:
- Educational content on blockchain fundamentals
- Technical foundations relevant to Mitosis ecosystem
🚨 TL;DR
Data Availability (DA) is a critical, yet often overlooked component of modular blockchain architecture. For cross-chain protocols like Mitosis, DA is not just a theoretical concern — it's essential for secure, scalable, cross-chain liquidity and computation.
🔗 This article goes beyond the content on Mitosis University and Mitosis docs to explain how DA layers like Celestia and EigenDA shape the future of modular chains, and why understanding them is crucial for building on or using Mitosis.
🧩 What is Data Availability?
Data Availability refers to the ability of a blockchain network to make all transaction data publicly accessible so anyone can verify the state of the chain.
In monolithic blockchains (e.g., Ethereum pre-rollups), execution, consensus, and DA are bundled together.
But in modular blockchains, these layers are separated:
📌 Learn more: Modular vs. Monolithic blockchains (Celestia docs)
📊 Diagram 1: Modular Blockchain Stack
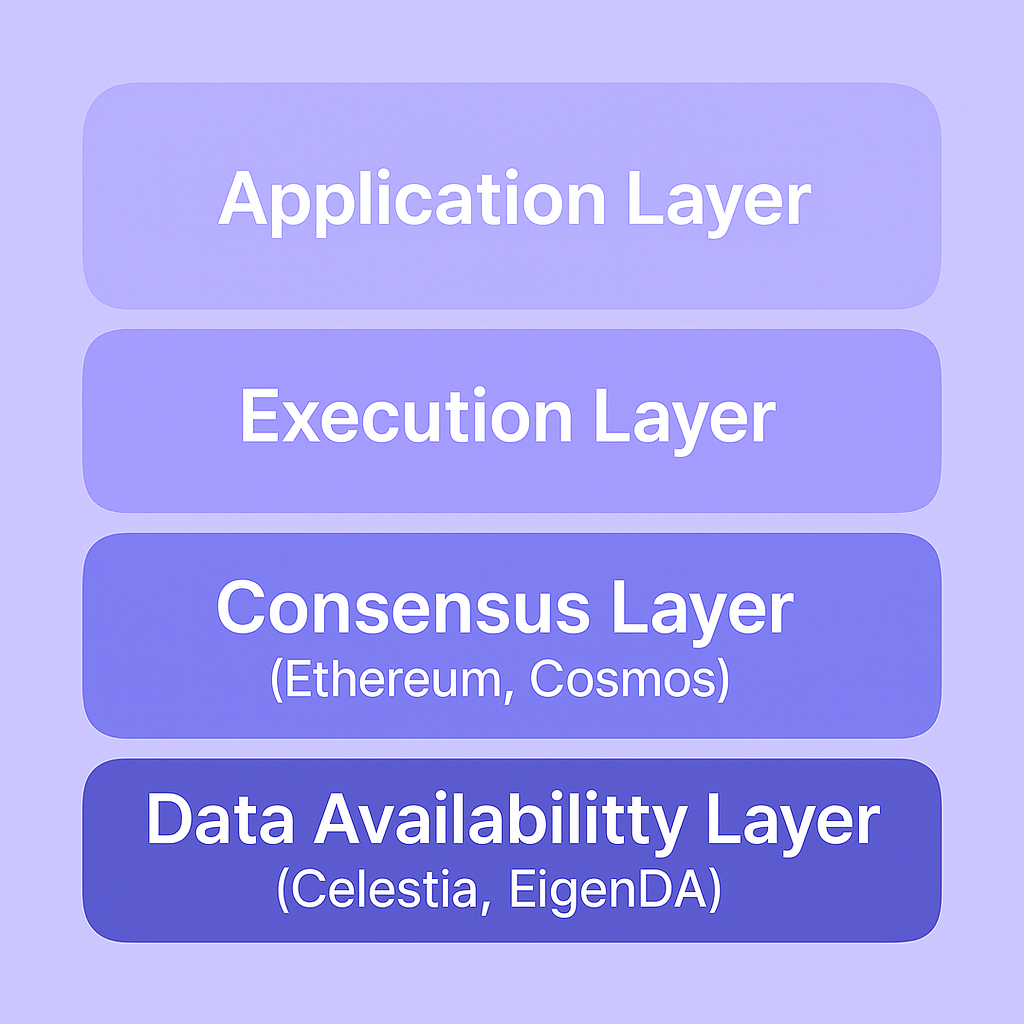
🔄 Why Data Availability Matters for Mitosis
Mitosis connects multiple blockchains and enables programmable cross-chain liquidity. That means Mitosis nodes need to verify state transitions on connected chains to move assets safely.
But here's the catch:
To verify anything, you must be able to access the data that proves what happened.
If a rollup says, “User deposited 10 ETH,” Mitosis can’t just take its word — it needs to verify the proof, which requires data availability.
🌐 Cross-Chain DA in Practice
Let's walk through a real-world scenario.
🧪 Scenario:
- Rollup A posts data to Celestia.
- Rollup B posts data to EigenDA.
- Mitosis bridges the two.
Mitosis must verify Rollup A's data to process transfers to Rollup B.
🔗 Reference: Celestia DA architecture 🔗 Reference: EigenDA onchain data commitments
If Rollup A’s DA layer goes offline, Mitosis cannot validate the proofs, and asset safety is compromised.
🧠 Diagram 2: Mitosis Bridging Two Rollups with DA layers
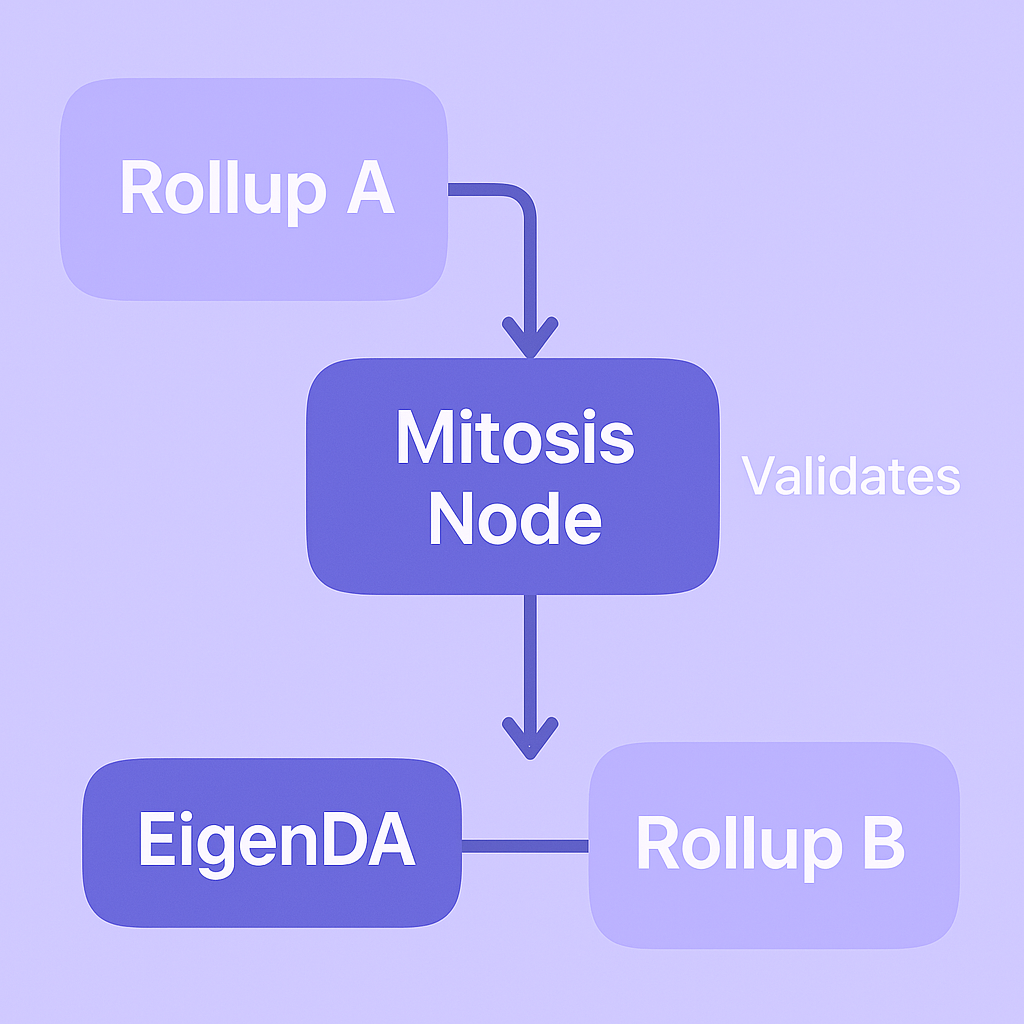
🛡️ How DA Layers Ensure Availability
Modern DA layers use Erasure Coding and Data Availability Sampling (DAS) to scale without sacrificing security.
🧪 Erasure Coding
Erasure coding breaks data into chunks + parity pieces. If part of the data is missing, it can be reconstructed.
🔗 Deep dive: Erasure coding in Celestia
🔍 Data Availability Sampling
Instead of downloading all data, light clients sample small random pieces.
If enough samples are available, you can be statistically confident the whole block is available.
🔗 Research paper: Fraud and Data Availability Proofs
📊 Diagram 3: Data Availability Sampling
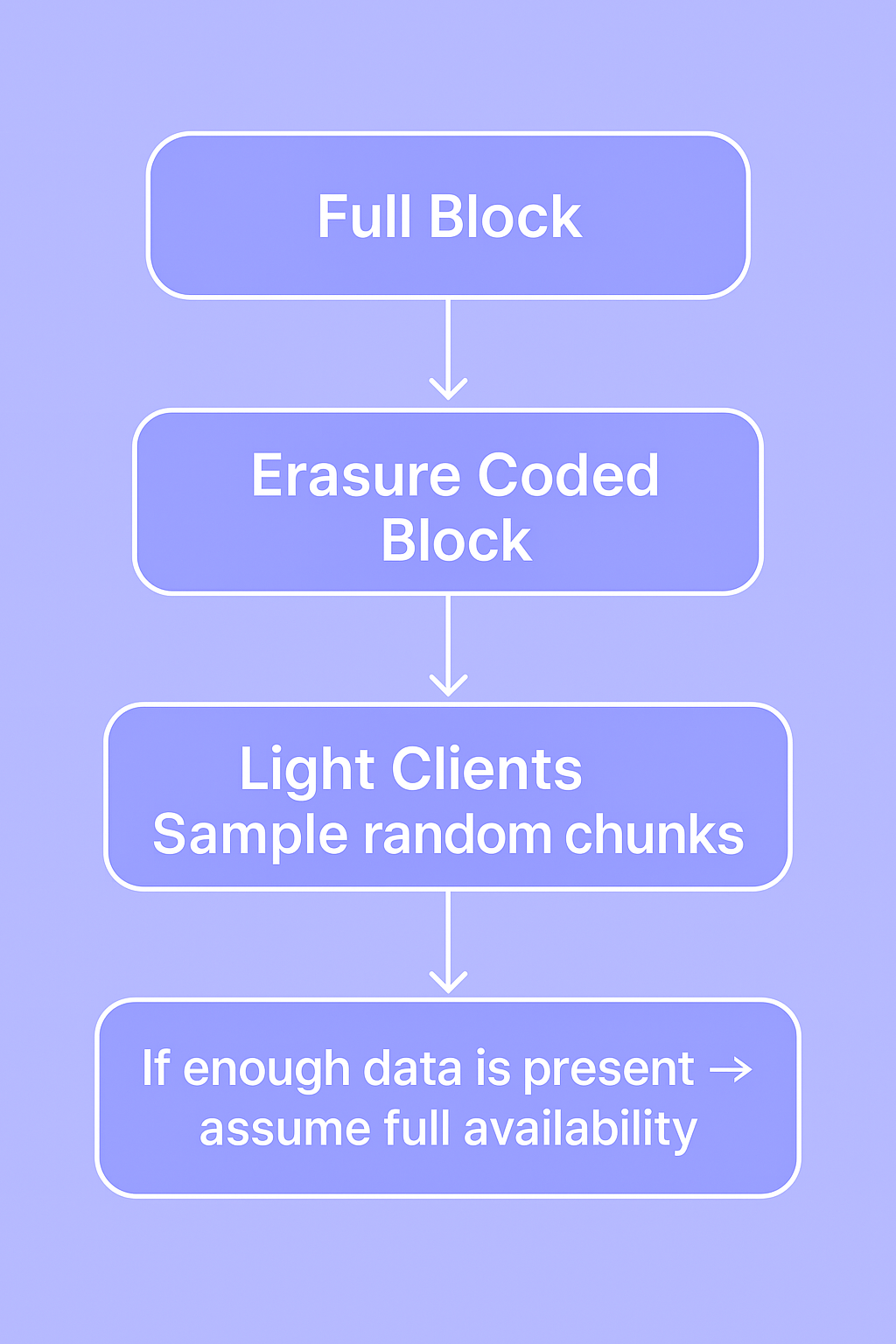
🧑💻 What This Means for Mitosis Builders
As a user or developer interacting with the Mitosis liquidity layer, you should:
- ✅ Check the DA guarantees of any rollup or chain you bridge.
- ✅ Prefer chains using robust DA layers (e.g. Celestia, EigenDA).
- 🚫 Avoid rollups that store data off-chain or on centralized servers.
Because if a chain’s DA fails, your assets could be locked or lost, and Mitosis cannot safely validate state transitions.
🚀 Conclusion
Cross-chain DA is the invisible pillar that holds modular ecosystems together.
Mitosis depends on this pillar to provide safe, scalable programmable liquidity across chains.
If you're building in the new era of modular, multichain DeFi, you must understand how DA works — and choose your stack wisely.
✅ Further Reading
- What is Data Availability? (Celestia)
- EigenDA Overview
- Data Availability and Light Clients – Vitalik Buterin
- Mitosis Documentation
Comments ()