Crypto Bridging Unveiled: Your Ultimate Guide to Seamless Blockchain Interoperability

Introduction
As blockchain ecosystems evolve, the demand for interoperability has never been more urgent. With thousands of blockchains operating independently—often on different protocols—users and developers face limitations when trying to move assets or data between them.
Crypto bridging has emerged as a vital solution, allowing seamless asset transfers across chains. Whether you're a DeFi investor, NFT collector, or developer, understanding crypto bridges is crucial to unlocking the full potential of the decentralized world.
This guide explores how crypto bridges work, the various types, their benefits and risks, and how they’re being used in the real world today.
What Is Crypto Bridging?
Crypto bridging refers to protocols or services that enable the transfer of digital assets—like tokens, stablecoins, or NFTs—between two or more blockchains that don’t natively communicate.
For example, a bridge might let you move ETH (Ethereum) to the Solana network or transfer Bitcoin to Ethereum in the form of Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) for use in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
Bridges act as connectors, enabling interoperability by mimicking assets on a destination chain while locking or burning the original assets on the source chain. This mechanism unlocks broader use cases and liquidity across ecosystems.
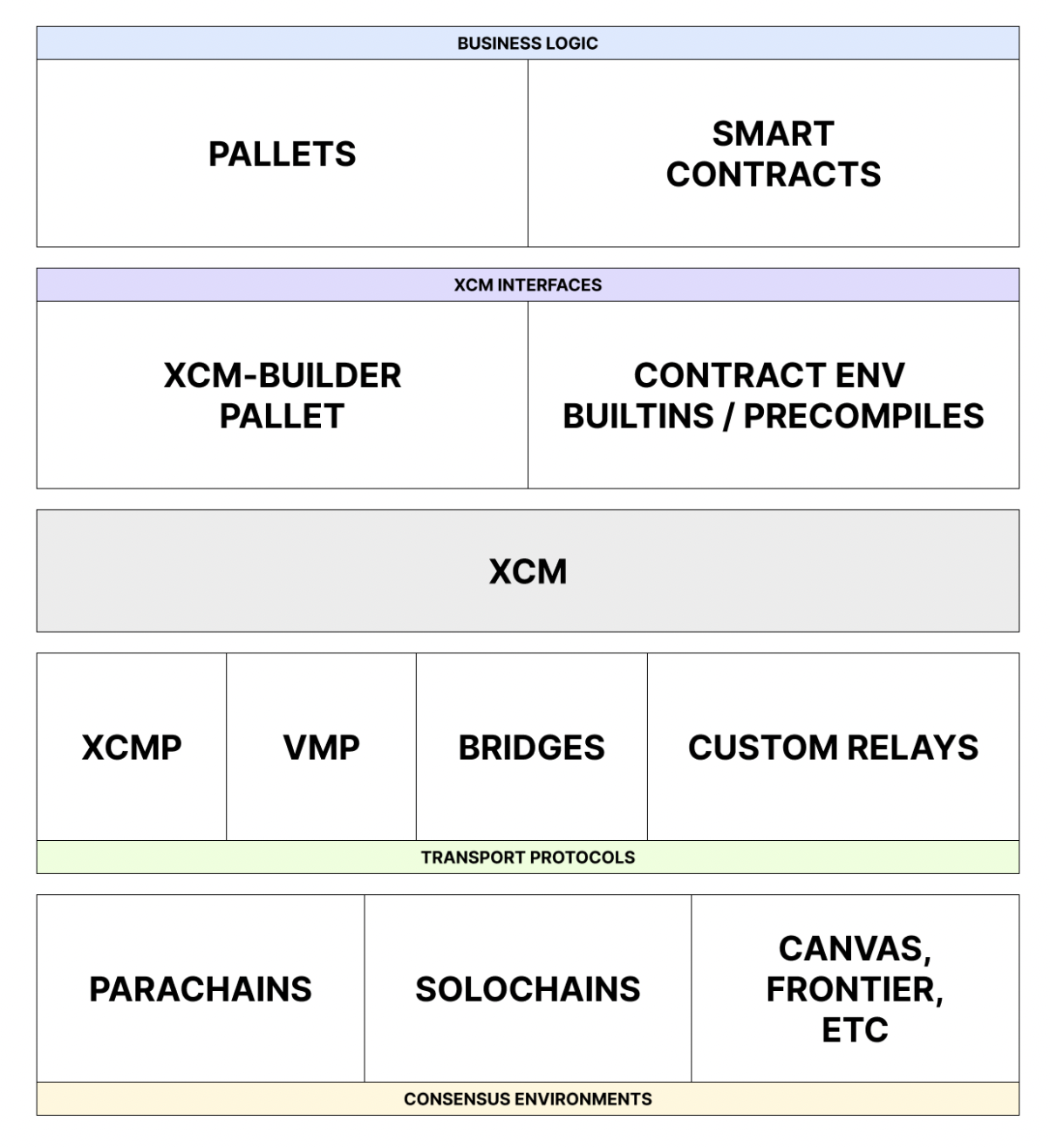
How Do Crypto Bridges Work?
While implementation may vary, most bridges follow a core process:
1. Asset Locking or Wrapping
- On the source chain, the asset is locked or burned.
- A corresponding wrapped version (e.g., WBTC on Ethereum) is minted on the destination chain.
2. Cross-Chain Verification
- Smart contracts, oracles, or validator nodes confirm that the original asset is locked or burned securely.
- This step ensures that minting on the new chain mirrors real value.
3. Asset Release or Minting
- Once verification is complete, the bridge protocol mints or releases the asset on the target chain for use.
4. Reverse Transfers
- Moving assets back involves burning the wrapped token on the destination chain and releasing the original on the source chain.
Types of Crypto Bridges
🏦 Custodial Bridges
- Managed by centralized entities (e.g., Binance Bridge, WBTC).
- Simpler to use but require trusting a third party.
🔐 Non-Custodial Bridges
- Rely on smart contracts or decentralized validators (e.g., Wormhole, Across Protocol).
- Trustless and decentralized, but more complex.
🔗 Native Bridges
- Developed within specific blockchain ecosystems (e.g., Polygon Bridge for Ethereum-Polygon).
- Seamless and efficient within supported chains.
💧 Cross-Chain Liquidity Bridges
- Use liquidity pools to allow fast token swaps (e.g., Synapse, Stargate).
- Great for DeFi use cases.
🌐 Generalized Bridges
- Support data and asset transfers beyond tokens (e.g., Polkadot’s XCM, Cosmos IBC).
- Enable broader interoperability and governance.
Benefits of Crypto Bridging
- Interoperability: Connect otherwise isolated chains to enhance collaboration and composability.
- Liquidity Expansion: Aggregate liquidity across networks, fueling trading, staking, and lending.
- Broader Use Cases: Access DeFi on Ethereum, NFTs on Solana, or fast transactions on Layer 2 chains.
- Cost Optimization: Bridge to low-fee chains to avoid high gas costs.
- DeFi & NFT Innovation: Cross-chain apps and marketplaces are expanding rapidly.
Risks and Challenges
- Security Threats: Bridges are high-value targets. Exploits like the $600M Ronin Bridge hack emphasize the need for strong security.
- Centralization Risks: Custodial bridges introduce trust dependencies and regulatory exposure.
- Complex User Experience: Mistakes can lead to lost funds, especially when addresses or chains are mismatched.
- Liquidity Fragmentation: Poorly funded liquidity pools can cause slippage or failed swaps.
- Regulatory Gray Areas: Custodial bridges and large-volume transfers may face future regulation.
Best practices: Use audited protocols, start with small amounts, and double-check all details before bridging.
Top Crypto Bridges in 2025
- Wormhole: Decentralized, multi-chain support (Ethereum, Solana, Aptos). Great for NFT bridging.
- LayerZero: Lightweight, secure omnichain messaging and bridging.
- Polygon Bridge: Fast, cost-effective asset transfers between Ethereum and Polygon.
- Synapse Protocol: Liquidity-based bridge with fast token swaps and stablecoin support.
- Cosmos IBC: Supports full data and asset interoperability within the Cosmos network.
Real-World Applications
💱 DeFi Access
Move stablecoins or tokens between ecosystems to chase yields or access exclusive protocols.
🎨 NFT Marketplaces
Transfer NFTs cross-chain to participate in different platforms or ecosystems.
🎮 Blockchain Gaming
Enable players to use in-game assets across multiple games or chains.
🏢 Enterprise Solutions
Use bridges for supply chain transparency, cross-chain asset tracking, and private-public network integration.
🗳️ Cross-Chain Governance
DAOs can implement voting systems that span multiple blockchain networks via bridge messaging.
Using Crypto Bridges Safely: A Quick Guide
- Choose a Reputable Bridge: Look for security audits, experienced teams, and community trust.
- Ensure Wallet Compatibility: Use wallets like MetaMask, Phantom, or Trust Wallet based on your chains.
- Verify Contracts: Use official links or explorers to confirm contract addresses.
- Start Small: Test the bridge with a small amount to learn the process.
- Track Transactions: Use block explorers to confirm transfer status.
- Stay Informed: Monitor project updates or vulnerabilities through platforms like X (Twitter), Discord, or their official sites.
The Future of Crypto Bridging
The next evolution of bridging technology is already underway:
- Improved Security Models: Zero-knowledge proofs and multi-sig validators are strengthening bridge architecture.
- Omnichain Standards: Protocols like LayerZero and Chainlink’s CCIP are setting unified cross-chain standards.
- Layer-2 Ecosystem Growth: Bridges will increasingly connect Ethereum rollups and other L2s for cheap, fast transactions.
- AI Optimization: Smart routing for liquidity and fees could be handled by AI algorithms in the future.
- Regulatory Integration: Transparent, compliant bridges may become mainstream as crypto regulation evolves.
Conclusion
Crypto bridging is a cornerstone of blockchain interoperability, offering users and developers unprecedented flexibility across networks. As multi-chain ecosystems become the norm, bridges will underpin everything from DeFi to gaming to enterprise adoption.
References













Comments ()