Crypto Liquidity Pools, Impermanent Loss, and DeFi Innovation

Understanding Crypto Liquidity Pools
Crypto liquidity pools are smart contracts on blockchain platforms that hold reserves of cryptocurrencies, enabling decentralized trading without intermediaries. Managed by Automated Market Makers (AMMs), these pools facilitate token swaps by maintaining liquidity through algorithmic price determination. A key example is Uniswap, where users can trade ETH for USDC by interacting with a pool that holds both assets.
The operation relies on the constant product formula, X * Y = K, where X and Y are the reserves of two tokens, and K is a constant. For instance, if a pool starts with 10 ETH ($2,000 each) and 20,000 USDC ($1 each), the total value is $40,000, and K = 200,000. When a trade occurs, the reserves adjust to maintain K, ensuring price stability and liquidity.
Liquidity providers (LPs) deposit assets into these pools, receiving LP tokens that represent their share. They earn trading fees, typically 0.3% per trade on Uniswap, incentivizing participation. However, the value of their position can fluctuate due to price changes, leading to impermanent loss, a critical risk discussed below.
Mechanics of Liquidity Pools
The mechanics of liquidity pools are driven by AMM algorithms, which eliminate the need for traditional order books. The constant product formula ensures that as one token’s reserve increases, the other decreases proportionally, maintaining equilibrium. For example, if ETH’s price rises to $4,000, the pool might rebalance to ~7.07 ETH and ~28,284 USDC, totaling $56,568, reflecting market dynamics.
Key factors influencing pool mechanics include:
- Pool Depth: Larger pools minimize price impact from trades, reducing slippage.
- Asset Correlation: A Higher correlation between assets (e.g., BTC/ETH at 0.81 correlation) reduces impermanent loss risk.
- Trading Fees: Fees, like Uniswap’s 0.3%, reward LPs and can offset losses, especially in high-volume pools.
LPs can withdraw assets anytime, but the value may differ due to price movements, highlighting the importance of understanding pool dynamics.
Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss is a significant risk for LPs, occurring when the price of assets in the pool diverges from their initial deposit prices. It’s calculated using the formula:
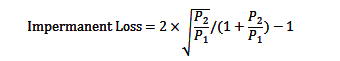
Where P_1is the initial price ratio, and P_2is the ratio at withdrawal. For example, if ETH doubles from $1,000 to $2,000, the loss is approximately 5.7%. This loss increases with greater price divergence: a 3x change results in 13.4% loss, and a 4x change in 20% loss.
Impermanent loss is “impermanent” because it can be reversed if prices return to original levels before withdrawal. However, it becomes permanent if the LP withdraws during unfavorable conditions. Research suggests up to 50% of Uniswap V3 users experience losses, with volatile pairs seeing 70-75% loss, while stablecoin pairs (e.g., USDC/USDT) face minimal risk due to low volatility.
Examples illustrate the impact:
- In an ETH/USDC pool, if ETH rises, the LP gets more USDC but less ETH, potentially worth less than holding ETH.
- Stablecoin pools, like those on Curve, minimize loss due to price stability, making them attractive for risk-averse LPs.
DeFi Innovations Addressing Impermanent Loss
As DeFi evolves, innovations have emerged to mitigate impermanent loss, enhancing LP attractiveness:
- Stablecoin Pools: Platforms like Curve Finance focus on stablecoin trading, reducing volatility. For instance, a USDC/USDT pool maintains near-constant value, minimizing loss.
- Correlated Asset Pairs: Pairing assets with high correlation, such as BTC/ETH, reduces loss since prices move together. Studies show a correlation of 0.81, lowering risk.
- Impermanent Loss Protection (ILP): Protocols like Bancor V2 allocate 15% of trading fees for insurance, covering potential losses. This mechanism, detailed at Bancor, protects LPs.
- Dynamic Liquidity Management: Pendle Finance, with a TVL of $2.4 billion, allows yield trading, hedging against volatility. Learn more at Pendle Finance.
- Single-Sided Liquidity Provision: DODO’s PMM algorithm enables single-token provision, reducing exposure. It offers better price stability, detailed at DODO.
- Cross-Chain Liquidity: Thorchain’s Continuous Liquidity Pools (CLPs) use RUNE for cross-chain swaps, addressing fragmentation, as noted at Thorchain.
- Off-Chain Transactions: Liquidity Network uses payment channels for faster, cheaper transactions, improving scalability, as discussed at Liquidity Network.
Recent Developments
As of Q2 of 2025, DeFi continues to innovate, with recent developments shaping liquidity pools:
- AAVE’s Surge: AAVE surged 21% to $220.48, driven by the Clarity for Payment Stablecoins Act, boosting stablecoin adoption and liquidity, as reported at Coin Push.
- Kraken’s Expansion: Kraken launched EU derivatives with a Cypriot license (CySEC), potentially attracting institutional liquidity.
- Bitcoin Dominance and Altseason: Bitcoin dominance at 60% early 2025 signals potential altseason, increasing DeFi activity, as noted at Coin Push.
- AI Tokens and Exchanges: Reports on AI tokens and top exchanges for 2025 highlight technological integration, influencing pool dynamics, as seen at Coin Push.
- Innovative Protocols: Convex Finance simplifies CRV rewards, and Liquidity Network addresses scalability, enhancing LP efficiency, as detailed at Blockchain Magazine.
Conclusion
Crypto liquidity pools are vital for DeFi, enabling decentralized trading while offering yield opportunities. However, impermanent loss remains a challenge, mitigated by innovations like stablecoin pools, ILP, and single-sided provision. Developments like AAVE’s surge and cross-chain solutions continue to shape this space, empowering LPs to navigate risks and maximize returns.
Key Citations
- Understanding Impermanent Loss in DeFi: A Comprehensive Guide for Liquidity Providers
- Impermanent Loss in DeFi: The Complete Guide
- What is Impermanent Loss? | Coinbase
- Liquidity pools and impermanent loss for dummies | r/CryptoCurrency
- Impermanent Loss In DeFi, Explained
- What is ‘Impermanent Loss’ in DeFi liquidity pools? | Coin Push Crypto Alerts
- The Best Crypto Liquidity Pools To Invest In For 2025 To Unlock Profits
- Impermanent loss explained: a guide for DeFi liquidity providers
- Impermanence Loss and Bancor V2 | Deribit Insights
- The Ultimate Guide to Impermanent Loss: Navigating Liquidity Provider Challenges | Swaap Finance
- What is Pendle Finance? | DataWallet
- Liquidity Pool Vulnerabilities in DeFi | ImmuneBytes
- AAVE Stablecoin Bill Passes Congress | Coin Push
- Kraken Launches EU Crypto Derivatives with Cypriot License | Coin Push
- Bitcoin Dominance Soars: When Does Altseason Begin? | Coin Push
- AI Tokens and Coins in 2025: In-Depth Report | Coin Push
MITOSIS official links:
GLOSSARY
Mitosis University
WEBSITE
X (Formerly Twitter)
DISCORD
DOCS



Comments ()