Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) in Crypto

Introduction
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have emerged as a transformative concept, redefining organizational structures within the crypto space. DAOs are member-owned communities without centralized leadership, managed by decentralized computer programs on a blockchain, such as Ethereum.
Defining DAOs: Core Concepts
A DAO is an organizational structure with no central governing body, popularized by blockchain enthusiasts, where members share a common goal and use a bottom-up management approach. They rely on smart contracts, self-executing code with rules encoded on the blockchain to manage operations and treasury, ensuring autonomy. For instance, DAOs are often described as crypto co-ops or group chats with bank accounts, highlighting their community-driven nature.
Key components include:
- Use of blockchain for a secure, tamper-resistant ledger, eliminating the need for trusted third parties.
- Governance is coordinated using tokens or NFTs, granting voting powers, with membership often tied to cryptocurrency wallet ownership.
- Aims to be open platforms where individuals control identities and data, potentially replacing public documents like deeds if regulatory structures permit.
Operational Mechanics: How DAOs Function in Crypto
DAOs operate on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, governed by smart contracts that define rules and hold the treasury. They raise capital by selling governance tokens, which grant membership and voting rights, typically with more tokens equating to more votes. Members can submit proposals, voted on by token holders, with decisions executed automatically via smart contracts.
For example, Lido DAO governs Lido Finance, where LDO token holders vote on operations through a process involving research forums, Snapshot voting (7 days, can’t end on weekends, 24 hours before on-chain execution), and Aragon for final voting (72 hours, 48 hours for/against, 24 hours objection phase, needs >5% token supply "Yes" and >50% of votes "Yes" as noted in this article Introduction to Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). Multisig wallets may allow leadership actions without community votes, such as pausing protocols in emergencies.
Membership models vary, including token-based (e.g., MakerDAO using MKR token), share-based (e.g., MolochDAO), and reputation-based (e.g., DXdao), supporting diverse governance approaches like delegation, automatic transactions, or multisig - https://ethereum.org/en/dao/. This flexibility ensures DAOs can adapt to different crypto purposes, from decentralized exchanges to funding public goods.
Historical Context: Evolution and Notable Examples
The term DAO dates back to the 1990s but gained traction in 2013, with Bitcoin sometimes considered the first DAO, though modern DAOs are understood as smart contracts on blockchains. Vitalik Buterin proposed in 2015 that DAOs could run without human intervention on Ethereum, launched that year, marking a significant milestone as mentioned in Decentralized autonomous organization. A pivotal event was the launch of "The DAO" in 2016, a venture capital fund that raised over $150 million, which was hacked for about $50 million worth of ether, leading to an Ethereum hard fork to recover funds. This incident underscored both potential and risks.
Other notable examples include ConstitutionDAO, formed in 2021 to buy a U.S. Constitution copy, raising $40 million but failing to acquire the asset, proving that like-minded individuals could form and pursue endeavors. These cases illustrate DAOs’ evolution from theoretical concepts to practical, community-driven entities in crypto.
Benefits: Advantages of DAOs in Crypto
DAOs offer several advantages, enhancing organizational efficiency and inclusivity in the crypto space:
- Democratic Foundation: Requiring only a governance token and internet connection, DAOs enable global participation, democratizing decision-making
- Transparency: All decisions are logged on the blockchain, promoting altruistic voting and accountability, as seen with Ethereum’s tamper-proof smart contracts.
- Egalitarian Structure: Members can submit proposals, with some DAOs requiring minimum tokens (e.g., Uniswap at the), ensuring all can see and provide feedback, increasing personal investment in success.
- Efficiency and Innovation: Automating processes reduces overhead, fostering new collaboration models, like Gitcoin, providing over $40 million for digital public goods using hackathons and decentralized crowdfunding, as mentioned here World Economic Forum.
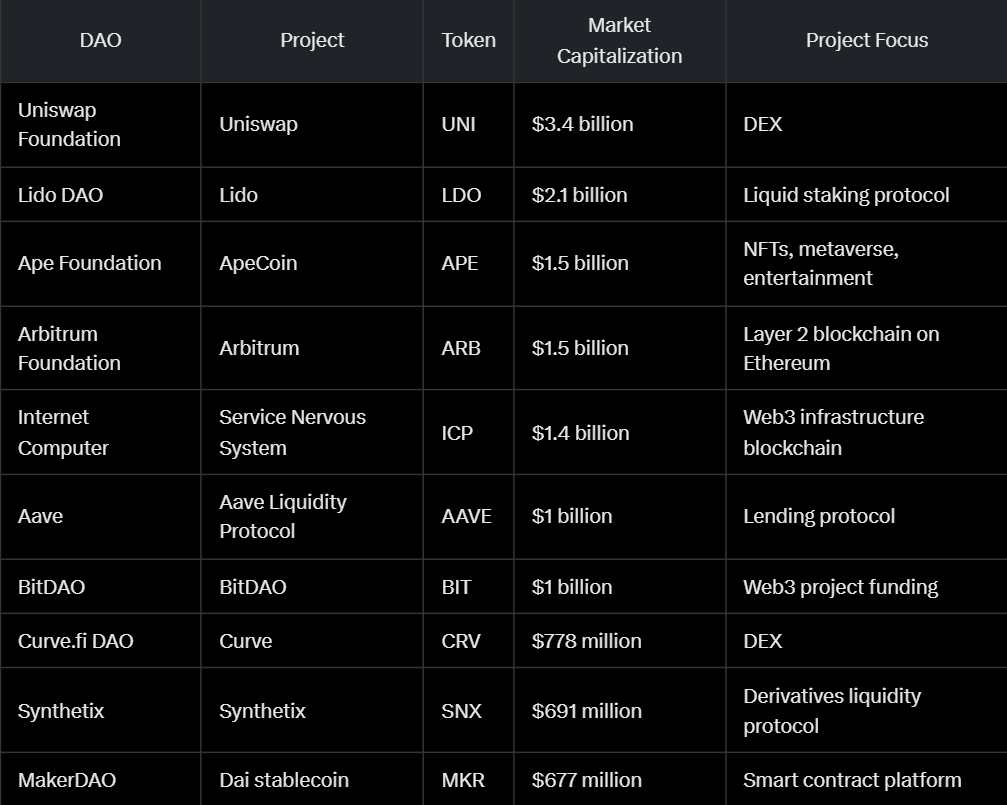
Top DAOs by governance token market capitalization in April 2023 included Uniswap ($3.4 billion), Lido DAO ($2.1 billion), and Ape Foundation ($1.5 billion), showcasing their scale and impact, as seen in the table below:
Challenges and Risks: Navigating Complexities in Crypto
Despite benefits, DAOs face significant challenges in the crypto space:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts can have bugs, as with the DAO hack, draining $50 million, highlighting cybersecurity risks. Chainalysis documented 125 crypto heists in 2022, with losses over $3 billion, a record year University of Miami.
- Governance Issues: Low voter engagement and concentration of voting power can undermine democracy, with operational complexity due to a lack of centralized management posing coordination problems World Economic Forum.
- Legal Uncertainty: The legal status is unclear, varying by jurisdiction, potentially preventing benefits like limited liability. Ooki DAO was sanctioned in September 2022 for illicit digital asset trading, violating registration and the Bank Secrecy Act, showing regulatory risks World Economic Forum.
- Operational Challenges: Managing DAOs requires technical expertise, and the lack of centralized leadership can lead to inefficiencies, especially in administration.
Future Prospects: Potential and Pathways Forward in Crypto
The future of DAOs seems promising, with ongoing efforts to address limitations. Jurisdictions like Wyoming, Vermont, and the Virgin Islands support legal status, with CityDAO buying 40 acres near Yellowstone using Wyoming’s DAO law. The World Economic Forum, with Wharton Blockchain and Digital Asset Project, launched the DAO Toolkit at Davos 2023, involving over 100 experts, aiming for clear, fit-for-purpose policy and oversight. Public-private cooperation is crucial to unlock responsible innovation, with DAOs managing billions in assets and engaging millions, as seen at DeepDAO.
As blockchain evolves, DAOs are likely to transform finance, governance, and social impact in crypto, but resolving legal and technical issues will be essential for their sustained growth.
Conclusion
DAOs represent a paradigm shift, offering democratic, transparent, and efficient collaboration models in crypto. While challenges like security and legal uncertainties persist, ongoing developments suggest a bright future, potentially reshaping decentralized systems.
Key Citations
- Decentralized autonomous organization - Wikipedia page
- Decentralized Autonomous Organization DAO definition - Investopedia
- Introduction to Decentralized Autonomous Organizations DAOs - Chainalysis blog
- What are Decentralized Autonomous Organizations DAO - Coinbase learn
- What are DAOs New York Times interactive feature
- What is a DAO Avast cybersecurity explanation
- What Are DAOs How Do They Operate Britannica Money
- What is a DAO Ethereum official documentation
- What is a Decentralized Autonomous Organization DAO TechTarget
- World Economic Forum DAOs decentralized autonomous organizations
- Cryptocurrency heists reach record high University of Miami news
- DeepDAO organizations overview
MITOSIS official links:
GLOSSARY
Mitosis University
WEBSITE
X (Formerly Twitter)
DISCORD
DOCS



Comments ()