Ecosystem-Owned Liquidity (EOL) vs. Matrix: Understanding Mitosis Liquidity Frameworks
Decentralized finance (DeFi) has revolutionized capital markets by making liquidity more accessible and programmable. However, maintaining sustainable liquidity remains a significant hurdle for protocols. Liquidity providers (LPs) often chase short-term incentives, leading to inefficient capital allocation and mercenary liquidity, where LPs migrate from one opportunity to another, draining projects of stability. Mitosis has introduced two liquidity provisioning models to address these inefficiencies: Ecosystem-Owned Liquidity (EOL) and Matrix. While both frameworks aim to optimize liquidity distribution, they differ fundamentally in structure, governance, and incentives.
EOL operates as a community-governed liquidity reserve, ensuring long-term liquidity sustainability for DeFi protocols. In contrast, the Matrix framework introduces curated liquidity campaigns, allowing LPs to participate in shorter-term, higher-yielding liquidity strategies. Both models have their distinct advantages, and understanding their mechanics is crucial for LPs, DeFi projects, and ecosystem builders.
This article explores the governance and liquidity dynamics of EOL, compares it with Matrix campaigns, and examines the Theo Network’s integration within the Matrix framework.
How EOL Governance Works and Its Impact on DeFi Liquidity
EOL is designed to create sustainable, protocol-owned liquidity, reducing reliance on external LPs who may withdraw liquidity at any moment. Unlike traditional liquidity mining programs that offer inflationary token rewards to LPs (often leading to sell pressure), EOL pools capital from the ecosystem and deploys it strategically based on community governance.
The governance mechanism of EOL is driven by Mitosis Improvement Proposals (MIPs), which allow token holders to vote on where, how, and when liquidity should be deployed. This collective decision-making ensures that liquidity flows align with long-term protocol health rather than short-term speculation. Key governance mechanics include:
- Liquidity Allocation Proposals: Token holders can propose and vote on liquidity deployment strategies, ensuring capital efficiency and risk management.
- Yield Optimization Strategies: The governance framework enables the selection of high-yield liquidity pairs and pools that maximize returns without excessive exposure to impermanent loss.
- Revenue Sharing & Sustainability: A portion of the generated yield is reinvested into the ecosystem, ensuring self-sustaining liquidity.
The impact of EOL governance extends beyond Mitosis. It stabilizes liquidity for DeFi projects, fosters protocol-owned liquidity reserves, and reduces dependency on external market incentives. By keeping liquidity within the ecosystem, EOL mitigates the risks associated with liquidity drainage and short-term capital flight. This approach is crucial for protocols aiming to build deep, reliable liquidity without excessive dilution of their native tokens.
Matrix Liquidity Campaigns and How They Differ from EOL
While EOL focuses on governance-driven liquidity management, Matrix provides an alternative for protocols seeking short-term, high-yielding liquidity injections. Instead of pooling funds into a central treasury, Matrix operates through targeted liquidity campaigns where protocols offer fixed incentives in exchange for LP participation.
Unlike EOL, where governance determines liquidity allocation, Matrix allows LPs to select specific campaigns that align with their risk appetite. The campaigns feature structured lock-up periods, during which LPs earn predefined rewards such as governance tokens, fixed yields, or additional DeFi incentives. Matrix campaigns are particularly attractive for DeFi startups and established protocols looking to bootstrap liquidity without relying on long-term commitment structures.
Theo Network Matrix Integration
The Theo Network’s partnership with Mitosis exemplifies how Matrix liquidity campaigns can be leveraged to drive targeted liquidity provisioning. The Theo Straddle campaign on the Matrix framework introduces a multiphase liquidity deployment strategy, ensuring capital efficiency while rewarding early adopters.
Eligibility Requirements and Structure
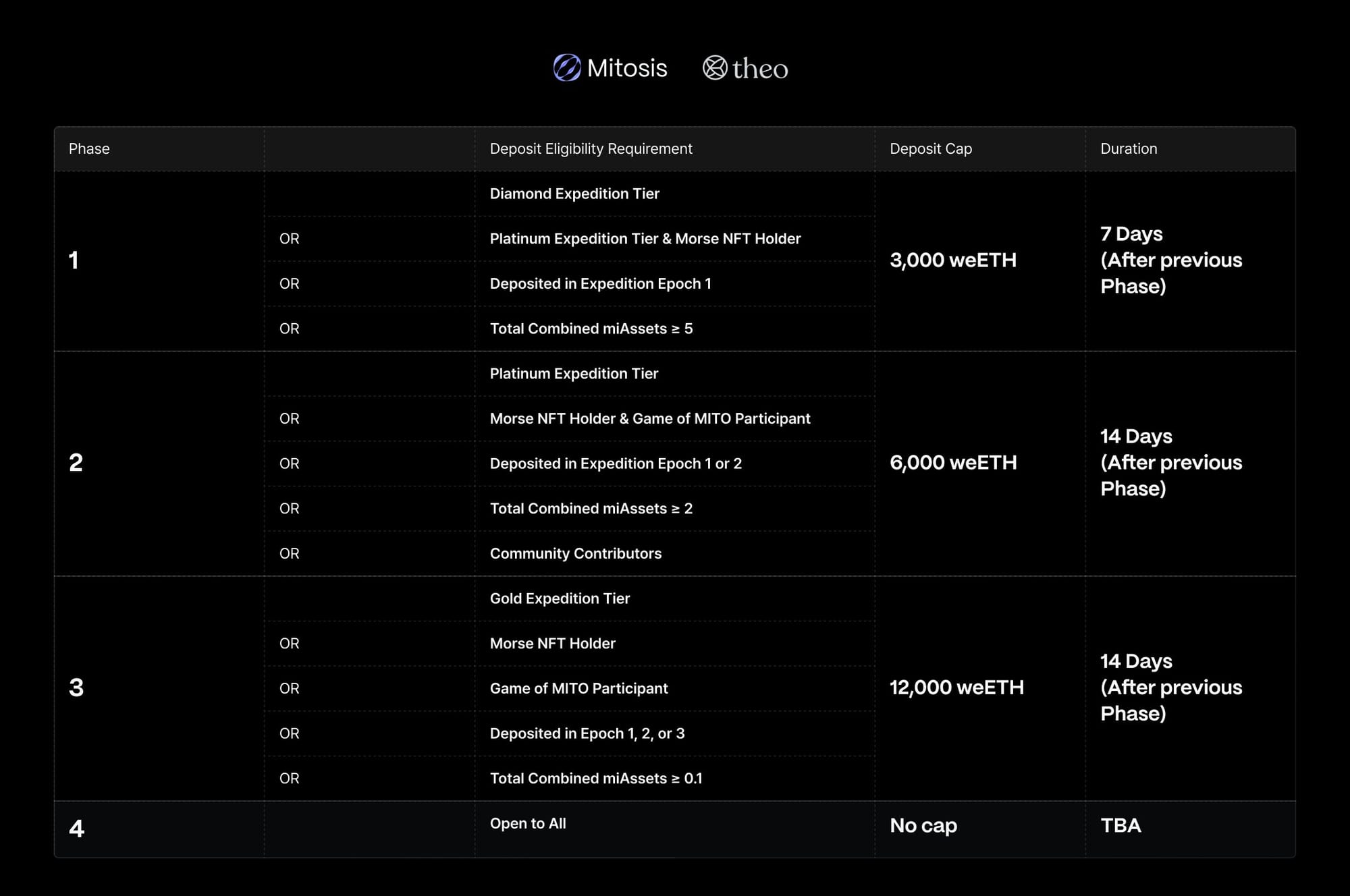
The Theo Straddle Matrix Vault is structured in four phases, each with different eligibility criteria and deposit caps:
Phase 1 (3,000 weETH cap, 7 days)
Diamond Expedition Tier
Platinum Expedition Tier & Morse NFT Holder
Deposited in Expedition Epoch 1
Total miAssets ≥ 5
Phase 2 (6,000 weETH cap, 14 days)
Platinum Expedition Tier
Morse NFT Holder & Game of MITO Participant
Deposited in Expedition Epoch 1 or 2
Total miAssets ≥ 2
Community Contributors
Phase 3 (12,000 weETH cap, 14 days)
Gold Expedition Tier
Morse NFT Holder
Game of MITO Participant
Deposited in Epoch 1, 2, or 3
Total miAssets ≥ 0.1
Phase 4 (No cap, TBA)
Open to all
Yield Mechanisms in the Theo Straddle Matrix Vault
Participants in the campaign receive maAssets, tokenized representations of their locked liquidity. These maAssets can be used in other DeFi strategies while still earning rewards from the Theo Straddle campaign. Yield opportunities include:
- Straddle Yield: A return generated from the Theo Network’s strategic trading operations.
- Theo Tokens: Additional rewards to incentivize participation.
- Mitosis Points: Boosted incentives within the Mitosis ecosystem, which may offer governance rights or further yield benefits.
By integrating with the Matrix framework, Theo Network ensures that liquidity commitments are met with structured incentives, making it attractive for LPs while providing deep liquidity for Theo’s operational needs.
Governance Mechanics of Liquidity Distribution in EOL
EOL’s governance is based on decentralized decision-making, ensuring that liquidity allocation aligns with the broader Mitosis ecosystem. Token holders have the power to propose, vote, and execute liquidity allocation strategies, optimizing for both risk and return.
Key Governance Mechanisms in EOL
Voting Power & Proposal System: Liquidity decisions are made through Mitosis Improvement Proposals (MIPs), where community members submit and vote on allocation strategies.
- Automated Liquidity Deployment: Once approved, EOL smart contracts automatically allocate liquidity based on the voted strategy, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
- Revenue Reinvestment: A portion of the yield generated from EOL’s liquidity provisioning is reinvested to strengthen the ecosystem’s liquidity reserves.
Unlike Matrix, where LPs individually choose liquidity opportunities, EOL relies on collective governance to direct capital to strategic liquidity pools. This makes EOL ideal for long-term liquidity sustainability, while Matrix remains suited for time-sensitive liquidity campaigns that prioritize short-term gains.
Conclusion
Mitosis’ dual liquidity frameworks, EOL and Matrix, address two critical needs in DeFi: sustainable, community-driven liquidity and targeted, high-yield liquidity injections. EOL’s governance model ensures that liquidity is strategically allocated and optimized, reducing reliance on mercenary LPs and fostering protocol-owned liquidity. On the other hand, Matrix introduces a flexible, campaign-driven approach, allowing LPs to engage with high-yield liquidity opportunities that suit their risk appetite.
The Theo Network’s Matrix integration illustrates how structured liquidity campaigns can be curated for maximum efficiency, offering incentives in a phased approach while ensuring deep liquidity for protocols.
As DeFi continues to evolve, liquidity strategies will remain central to protocol sustainability. Should protocols prioritize long-term, governance-driven liquidity management (EOL), or should they leverage flexible, high-yield liquidity campaigns (Matrix)? The answer may lie in a hybrid approach—one that combines the sustainability of EOL with the agility of Matrix, ensuring both short-term liquidity needs and long-term ecosystem stability.



Comments ()