Mitosis x Babylon: How They Can Provide the First Bitcoin Cross-Chain System, Technical Analysis

The cryptocurrency world has long been overdue for a secure and decentralized cross-chain infrastructure that can connect Bitcoin with more advanced smart contract networks. Despite numerous attempts to build a bridge between Bitcoin and other blockchains, there is still no truly trustless, permissionless, and censorship-resistant solution. However, the tandem of Mitosis and Babylon has the potential to change this paradigm.

Problem: Bitcoin Isolation
Bitcoin, as the largest and most reliable cryptocurrency, has colossal liquidity, but its architecture is not designed for native cross-chain interactivity. Unlike networks like Ethereum, Bitcoin does not have a built-in virtual machine (EVM), there are no standard methods for generating smart contracts, and there are no easy ways to prove the state of another chain.
Today's solutions - from wrapped BTC (WBTC) to bridges - are essentially centralized or partially trusted. This creates vulnerabilities to hacks and censorship, and goes against the core principles of decentralization.
Solution: Mitosis and Babylon symbiosis
The two projects, Mitosis and Babylon, are being developed as independent modules, but their potential is revealed in tandem:
Babylon: Bitcoin-anchored security layer
Babylon provides a Bitcoin timestamping and staking layer, allowing other blockchains to apply Bitcoin’s security without having to trust intermediaries. The main principles are:
• Finality via Bitcoin: chains can transfer their state to Bitcoin through special proofs, receiving finality tied to the network with the highest hash power.
• Bitcoin-based validator slashing: validators on networks using Babylon post collateral in BTC. If they act maliciously, this collateral can be destroyed, providing a strong economic incentive to act honestly.
• Separation of consensus and execution: Babylon does not perform its own computation, but provides a consensus and security layer.
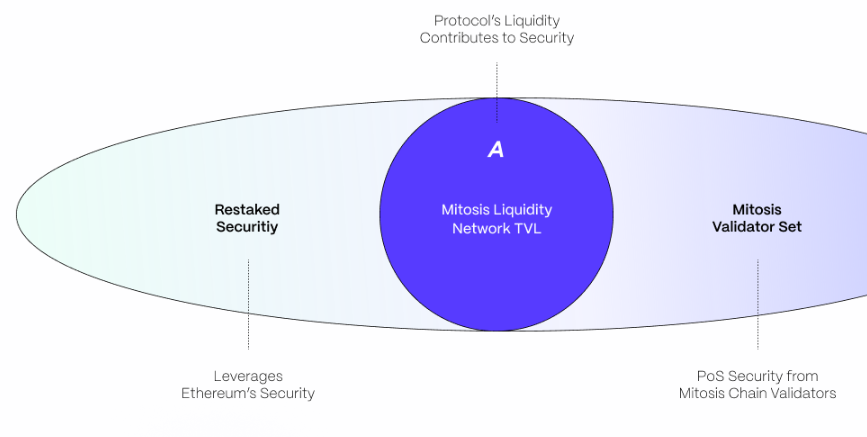
Mitosis: Cross-chain Liquidity and Execution Layer
Mitosis is an OMNI-layer protocol for cross-chain communication based on native L2 and zk-validated channels:
1. Universal liquidity via zk-channels: allows users to move assets between chains trustlessly and without the need for bridges, using zero-knowledge proofs.
2. Built-in compatibility with modular stacks: Mitosis can be used as a module in rollup ecosystems like Celestia, EigenLayer, Caldera, etc.
3. Execution via zkVM: arbitrary programs can be executed on the Mitosis network, which can then be proven and verified on another chain.

How it works: Mitosis + Babylon = trustless BTC bridges
The combination of these solutions allows for a decentralized and secure bridge between Bitcoin and other ecosystems:
Babylon provides finality and security
A network interacting with BTC can use Babylon to anchor the state and enforce slashing of validators' BTC collateral. This removes the need for centralized federations like WBTC.
Mitosis implements cross-chain execution and asset movement
Assets, including BTC or BTC derivatives, can be moved between chains via zero-knowledge proofs and Mitosis execution logic. Instead of “freezing” BTC in multisig, Mitosis creates a cryptographically verifiable wrapper that interacts with external state.
Bitcoin as a settlement layer and guarantor of validity
Since both Babylon and Mitosis can use Bitcoin as a finality layer, actions occurring in them can be independently verified and censorship-resistant.
Technical Overview: Mitosis x Babylon — Trustless Bitcoin Cross-Chain Architecture
|
Component |
Mitosis |
Babylon |
Combined Impact |
|
Primary
Function |
Cross-chain
execution and liquidity layer |
Bitcoin
timestamping and security layer |
Enables
trustless BTC movement and smart contract interoperability |
|
Security
Model |
Zero-knowledge
proof verification |
Bitcoin-based
validator staking and slashing |
Economic
and cryptographic guarantees without centralized custody |
|
Core
Technology |
zkVM,
zk-messaging, omni-layer channels |
Bitcoin
anchoring, staking layer, slashing via Bitcoin |
ZK +
Bitcoin anchoring = fully decentralized BTC interoperability |
|
BTC
Integration |
Enables
native BTC to move across chains using zk-lock contracts |
Uses
BTC for finality and validator collateral |
BTC is
both the asset and the security base |
|
Finality
Assurance |
ZK
proofs validated by target chain |
Anchoring
checkpoints in Bitcoin |
Bitcoin-level
finality for cross-chain actions |
|
Validator
Accountability |
Enforced
via ZK proof verification and message propagation |
Validators
slashable in BTC for malicious behavior |
High-stakes
validation backed by Bitcoin security |
|
Smart
Contract Support |
Customizable
zkVM for execution on any rollup or L2 |
No
execution layer; serves as consensus/finality layer |
Execution
(Mitosis) + Security (Babylon) = Full-stack dApp support |
|
Cross-Chain
Messaging |
Native
ZK-based messaging across chains |
N/A
directly, but secures state sync |
Trustless
message passing with Bitcoin-based settlement |
|
Use
Cases |
BTC in
DeFi, L2 liquidity routing, native cross-chain swaps |
Secure
L2s, timestamped checkpoints, slashing conditions |
Native
BTC in DeFi without wrappers or bridges |
|
Centralization
Risk |
Fully
decentralized with permissionless architecture |
Bitcoin-secured
consensus, no multisig or federations |
No
single point of failure, unlike WBTC/federated bridges |
|
Scalability |
ZK
rollups and recursive proofs |
Stateless,
scales with Bitcoin |
ZK tech
+ Bitcoin scale = high-throughput BTC cross-chain flows |
|
Upgradeability |
Modular,
supports plug-in apps and integrations |
Minimalist,
focused on finality and slashing logic |
Agile
application layer with stable security base |
|
Example
Workflow |
User
locks BTC → zkProof → minted token on L2 |
BTC
anchoring confirms zkProof and slashing conditions |
Seamless
trustless flow of BTC to any chain with auditability |
|
Regulatory
Benefits |
No
centralized custody = lower custodial risk |
Anchoring
to Bitcoin may be seen as more robust |
Transparent,
auditable, and user-controlled BTC flow |
|
Differentiator
from WBTC/Bridges |
No
wrapped tokens, no custodians |
No need
for third-party trust assumptions |
First
truly decentralized BTC cross-chain interoperability stack |
Use case: BTC in DeFi without wrapped tokens
Let's imagine a user wants to deposit BTC into a DeFi protocol on Ethereum L2:
1. They send BTC to a special zk-lock contract, the confirmation of which is transmitted to Mitosis zkVM.
2. Mitosis generates a lock proof and syncs it with the third-party chain via zk messaging.
3. Babylon ensures that this process is final in Bitcoin, and if there is an attempt to abuse it, validators lose their BTC collateral.
4. The user receives a “BTC-native” token on L2 and can use it without trusting a centralized custodian.
Conclusion
The Mitosis and Babylon pairing is a step toward creating a truly cross-chain system with native Bitcoin support, without wrappers, bridges, or trust in third-party intermediaries. Rather than adapting Bitcoin to other chains’ smart contract standards, these projects adapt other chains to Bitcoin’s fundamental principles: decentralization, finality, immutability.
In the coming months, these modular, zk-based, anchoring-based architectures will be the key to unleashing Bitcoin liquidity in DeFi. And perhaps for the first time, in a truly decentralized way.


Comments ()