Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake: How Blockchain Stays Secure

Ever wondered how Bitcoin or Ethereum stay safe and avoid hacks?
It’s all about how new blocks are added to the chain.
Let’s break it down in simple words
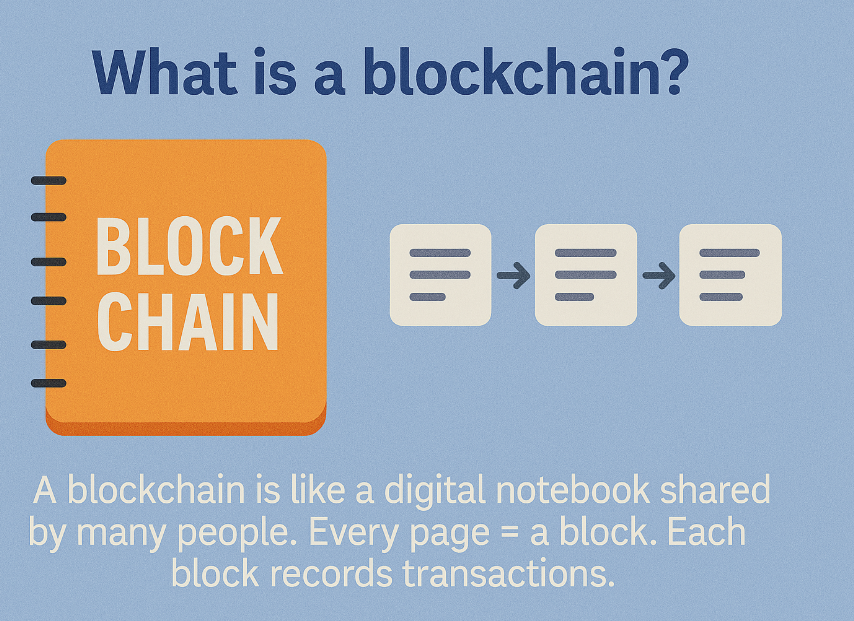
What is a blockchain
Blockchain is the tech behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
It stores all crypto transactions in blocks, linked together.
Once a transaction is added, it can't be changed — making it secure.
It lets people send and receive crypto without banks or middlemen
But how do we agree on what gets written in the notebook?
That’s where Proof of Work and Proof of Stake come in.
What is Proof Of Work (PoW)?
Proof of Work is a method used by like Bitcoin to confirm transactions.
It requires computers (called miners) to solve complex puzzles to add a new block.
The first miner to solve it gets rewarded with crypto.
This process uses a lot of energy but keeps the network secure and tamper-proof.
It helps prevent fraud and ensures only valid transactions are added.

PoW Example:
Imagine a classroom. The teacher says:
“I’ll give a prize to whoever solves this huge puzzle first.”
All students try at the same time.
Whoever finishes first gets a reward.
But it uses a lot of energy
What is Proof Of Stake (PoS)?

Proof of Stake is a way for blockchains to confirm transactions without using heavy computing power.
Instead of miners, it uses validators who “lock up” some of their crypto as a stake.
The network randomly picks one of them to approve the next block.
Honest validators earn rewards, while dishonest ones can lose their staked coins.
It’s energy-efficient and helps keep the network fast and secure.
PoS Example:
Back to the classroom.
Now, the teacher says:
“Everyone put some money in a jar. I’ll randomly pick one of you to win the prize.”
The more you put in the jar, the higher your chances to be picked.
Conclusion
Both Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are like security guards for blockchain.
PoW = strong but energy-hungry 💪⚡
PoS = smart and energy-saving 🌱🎯
Different tools for different goals — but both keep crypto safe.


Comments ()