The Benefits of Mitosis Liquidity Vaults Compared to Traditional Liquidity Pools: The Safer Choice for DeFi Users

Mitosis recently released their litepaper explaining the exciting plans they have for programming liquidity: providing liquidity to small scale protocols and rewarding investors for contributing to the Ecosystem-Owned Liquidity (EOL).
Today we'll look at the 'Mitosis Vaults'– one of the most intriguing aspects of the Mitosis Ecosystem.
Introduction
Since the inception of liquidity pools, acquiring investment from financial institutions has become a thing of the past. Decentralized Fiance (DeFi) has been a game changer that has impacted the way users provide and access liquidity, but it comes with its risks.
Security breaches, impermanent loss, and liquidity drain have plagued many DeFi liquidity providers. Traditionally, platforms like Uniswap and AAVE have relied on liquidity pools, where users deposit assets in exchange for rewards.
While effective, these pools come with vulnerabilities, including smart contract exploits and the inability to efficiently manage locked funds.
But everything is set to change with the infrastructure of Mitosis Vaults, which is proposed to be a next-generation liquidity management system that will tackle these security concerns while enhancing capital efficiency.
So what sets Mitosis Liquidity Frameworks apart from traditional pools? We will outline the critical differences of Mitosis Vaults from traditional liquidity pools, examine their security features, risks, and in general, their suitability for users of DeFi who are looking for a safer way to manage their assets.
Understanding Traditional Liquidity Pools (LP)
Before we dive into further, getting a better knowledge of how LPs work is necessary to fully grasp the gaps Mitosis hopes to bridge. In conventional DeFi liquidity models , users deposit tokens into automated market maker (AMM) or lending pools, where they earn rewards from trading fees.
How Do LPs Work?
In an LP system, users deposit their assets into smart contract-based pools, which are used for automated trading and lending. Take, for instance, an Automated Market Maker model; users can deposit two assets, either ETH or USDC, into a liquidity pool.
The AMMs use pricing algorithms to determine asset exchange rates based on supply and demand, which these deposited assets follow to facilitate token swaps and, in the long run, earn liquidity providers' trading fees.
Problems with Traditional LPs
Smart Contract Exploits
Liquidity pools use smart contracts or self-executing pieces of code that manage asset storage, trading, and their distribution within the DeFi protocol. Smart contracts remove the intermediary, but this also introduces new vulnerabilities to which hackers can begin malicious activiites.
Liquidity providers might remember the not-so-pleasant Mango Markets hack of 2022, wherein hackers leveraged the external oracles that DeFi protocols rely on to price assets and manipulated the price feed by spamming low-liquidity markets with fake trades. This tricked the smart contract into mispricing assets and draining liquidity pools.
Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss is the concealed cost that every liquidity provider of AMM pools, like Uniswap, Curve, and Balancer, has to put up with. It happens any time the price of one or both assets in the liquidity pool increases or decreases considerably after a deposit.
The larger the price swing, the more loss liquidity providers experience. While trading fees help compensate liquidity providers, they may not always offset the losses from price changes. If prices return to their original state, the loss disappears, but that's rarely the case in volatile markets.
Rug Pulls and Governance Attacks
DeFi may operate in a trustless environment, but it can still be manipulated. Some DeFi projects allow developers to retain control over liquidity pools or smart contracts. With this control, they can suddenly withdraw all liquidity, leaving users with worthless tokens.
Also, whales and flash loan attackers can buy a majority of governance tokens and propose self-serving changes. To put it in perspective, an attacker could easily vote to redirect funds to their wallet or modify withdrawal rules to prevent users from exiting liquidity pools.
Limitations of Traditional LPs
Locked Capital & Inflexibility
As a user, if you deposit assets into lending pools, your assets are locked into a smart contract and these funds become part of the liquidity pool's total balance and cannot be freely accessed until withdrawn.
This means you can't use your locked assets for other DeFi opportunities like staking, lending, or collateralizing loans. These funds will sit idle or could be underutilized in pools, preventing you from optimizing their returns.
Unstable Liquidity & Mercenary Behavior
Liquidity providers are more interested in chasing the highest returns than building an Ecosystem that profits users and protocols like the EOL system Mitosis is building ( read more about that here).
These LPs frequently move funds between platforms, creating "mercenary liquidity", where users deposit liquidity only as long as rewards are attractive. Now, if a protocol reduces its yield incentives, these liquidity mercs may quickly withdraw, leading to unstable Total Value Locked (TVL).
This is bad for protocols as they can't maintain consistent liquidity and have to rely on protocols that rely on temporary yield boosts instead of sustainable liquidity.
Lack of Transparency in Yield Distribution
It's been well known that whales get the cream of the crop incentives from LPs, many DeFi protocols do not provide clear insights into how rewards are calculated and distributed and these whales often receive preferential yields through private agreements with protocol developers.
So, while whales negotiate higher rewards, smaller investors earn less despite providing liquidity, making it hard for everyone to get equal opportunities, as protocols may favour certain users or groups, reducing fairness in DeFi.
Mitosis Vaults: A Liquidity Management System

Mitosis Vaults takes it to the next level by improving the efficiency, security, and flexibility of liquidity provisioning in DeFi. Unlike traditional liquidity pools, where assets are locked and often exposed to risks, Mitosis Vaults provide a structured way to deposit, manage, and utilize liquidity without sacrificing user control.
How Does the Vault Infrastructure Work?
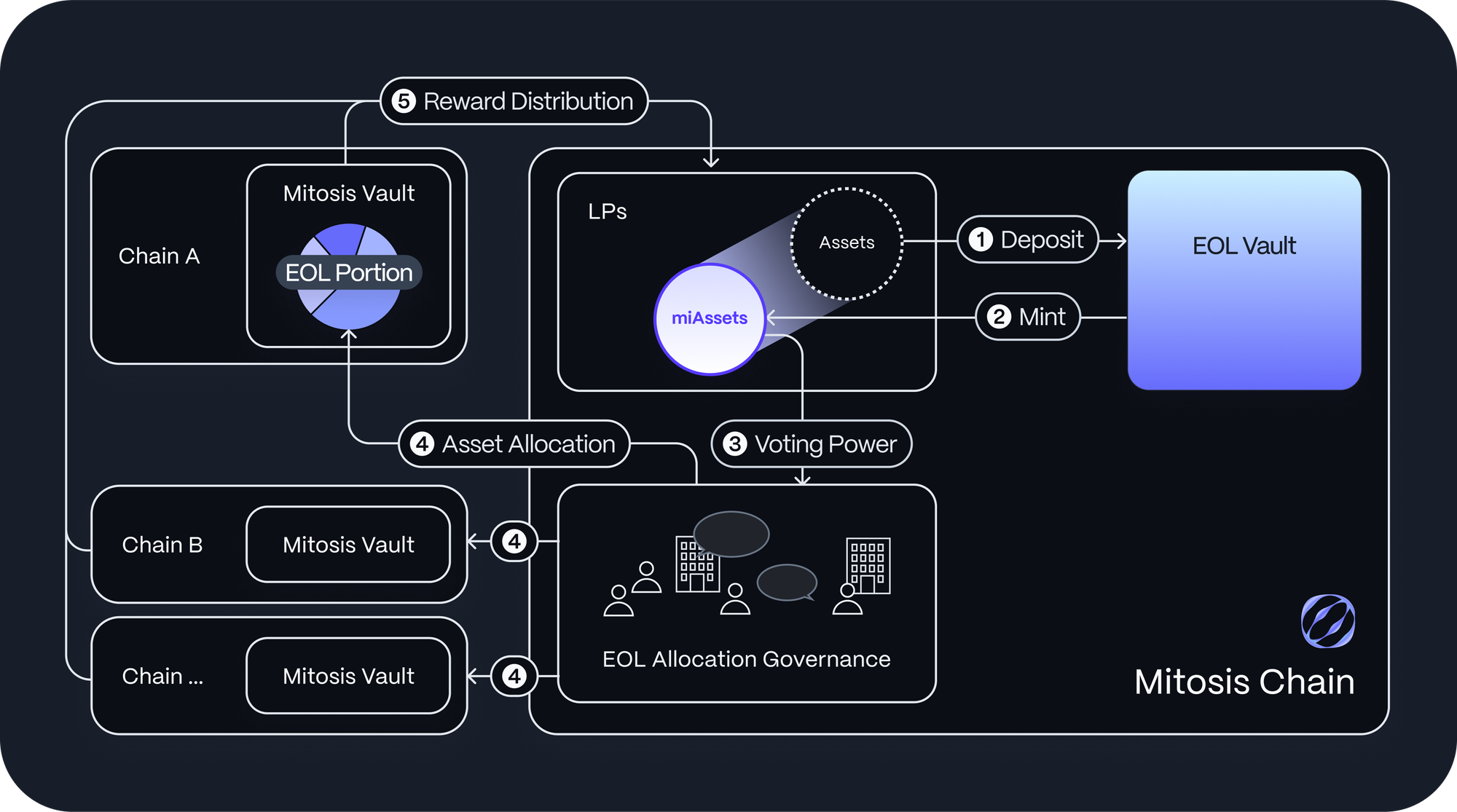
When a user deposits an asset (e.g., ETH, USDC) into a Mitosis Vault, the vault's smart contract receives and locks the deposited asset. The system transmits deposit data to the Asset Manager on the Mitosis Chain via a cross-chain message bridge.
The Asset Manager mints Vanilla Assets in a 1:1 tokenized representation for each deposited asset. The newly minted Vanilla Assets are then sent to the user's wallet on the Mitosis Chain.
With these vanilla assets, providers can pick from a catalogue of protocols with various yield opportunities to commit their Vanilla Assets. These assets are then locked and transferred to the DEFi protocol for yield generation, while MLF assets are issued to users in their place.
One great thing about this vault is if a user decides they want to withdraw their assets at any time, they can simply put in a request which will burn the corresponding Vanilla asset, reducing supply and releasing the original asset from the vault without any impact on the price or impermanent loss.
Mitosis Liquidity Frameworks (MLFs): Two Yield Strategies
Mitosis offers two different frameworks to providing liquidity through which users can maximize various strategies to make yields on their investments.
Ecosystem-Owned Liquidity (EOL)
The EOL allows users to supply and govern the collective liquidity pool and decide where to allocate assets. When a user deposits in the EOL system, they receive miAssets, which represent their share of the liquidity pool.
These assets grant users economic rights over the underlying assets and governance power, allowing them to vote on where and how liquidity is allocated.
Using miAssets, providers can vote on new protocols to be added to the system and determine how much liquidity goes into a project.
When it's time to be rewarded, users can be settled through the minting of new Vanilla Assets, increasing the value of their miAssets
In the event of a loss, the system burns Vanilla Assets from the EOL Vault, reducing the value of miAssets.
Matrix Liquidity Vault
On the other hand, the Matrix liquidity vault drives long-term incentives through tokenized liquidity. Here, users deposit their assets to receive 'maAssets'.
With these assets, they can track their claim on yield distributions and even use the maAssets in other DeFi applications to maintain capital efficiency.
Participants receive maAssets, and rewards are predefined, giving users more control over expected returns.
This vault ensures that users in for the long run are rewarded through a forfeiture mechanism.
For smaller protocols looking for funding this vault helps provide liquidity stability through a yield strategy that rewards compounded incentives based on long-term user behavior.
How Mitosis Vaults Solves Traditional DeFi Problems and Limitations.

Preventing Smart Contract Exploits
Mitosis Vaults use a layered approach where different components (deposit, supply, and utilize processes) operate separately, reducing the risk of full-scale breaches.
As the platform uses programmable liquidity markets, it reduces the reliance on price oracles that attackers often manipulate in traditional pools.
Unlike other pools, where liquidity sits openly in one smart contract, Mitosis Vaults lock assets securely and only move them based on predefined rules.
Mitosis smart contracts also undergo security audits and use governance-approved upgrades to fix vulnerabilities without disrupting user funds.
Eliminating Impermanent Loss
Instead of locking assets in an AMM pool where price changes create impermanent loss, Mitosis issues Vanilla Assets that maintain a 1:1 value ratio with deposited assets.
Mitosis assets are not fixed as well, giving providers flexibility toto withdraw, rebalance, or redeploy their liquidity without penalties.
Also, instead of earning rewards only through trading fees, Mitosis Vaults allocate assets to multiple DeFi strategies for higher, more stable returns, reducing the potential for impermanent loss.
Preventing Rug Pulls & Governance Attacks
Mitosis Vaults use decentralized governance and multi-signature security to prevent unauthorized asset movements, meaning developers cannot withdraw liquidity at will,
The Ecosystem-Owned Liquidity (EOL) system ensures that all governance decisions are gradual and publicly voted on, preventing hostile takeovers.
Users can always redeem their Vanilla Assets for the original deposited assets, meaning funds cannot be suddenly drained by insiders or malicious actors.
Solving Locked Capital & Inflexibility
Mitosis solves the issue of trapped user funds through Vanilla Assets—tokenized representations of deposited liquidity that remain fully usable to be traded, staked, used as collateral and moved through various chains while assets are locked in a Mitosis Vault.
Preventing Unstable Liquidity & Mercenary Behavior
Mitosis tackles mercenary liquidity by using governance-based liquidity allocation (EOL Vaults) and reward forfeiture mechanisms (Matrix Vaults).
Liquidity providers vote on where funds should be allocated using the EOL system, reducing dependence on temporary incentives and they can also withdraw funds anytime on the Matrix vaults, but forfeit unclaimed rewards if they leave early ensuring that protocols receive a stable stream of liquidity.
Improving Transparency in Yield Distribution
miAsset holders vote on liquidity allocation, making reward distribution fully transparent. All users earn the same proportional yield based on their miAsset or maAsset holdings, meaning no single user can make a backend deal to gain an advantage over other providers.
Finally, mitosis mints/burns Vanilla Assets based on protocol performance, ensuring real value-backed rewards instead of inflationary token emissions.
Why Mitosis Vaults Are the Future of Safe and Efficient DeFi Liquidity
As DeFi continues to evolve, liquidity management remains one of the greatest challenges for users and protocols alike and traditional Liquidity Pools - despite being the bedrock of DeFi - have some pretty big downsides.
Mitosis Vaults present a more secure, flexible, and transparent alternative. By tokenizing liquidity with Vanilla Assets, introducing governance-driven allocation (EOL Vaults), and implementing anti-mercenary mechanisms (Matrix Vaults).
Mitosis ensures capital efficiency, long-term liquidity stability, and fair reward distribution. It gives full ownership of the underlying assets allowing the participation in sophisticated yield strategies, and leverage in a system focused on long-term sustainability rather than short-term gains.
Through this innovative liquidity model, cross-chain functionalities and dedication to decentralization are sure to skyrocket; Mitosis Vaults will certainly set up the future of liquidity provisioning in DeFi.


Comments ()