The Stablecoin GENIUS Act: Trump’s Crypto Leap Forward
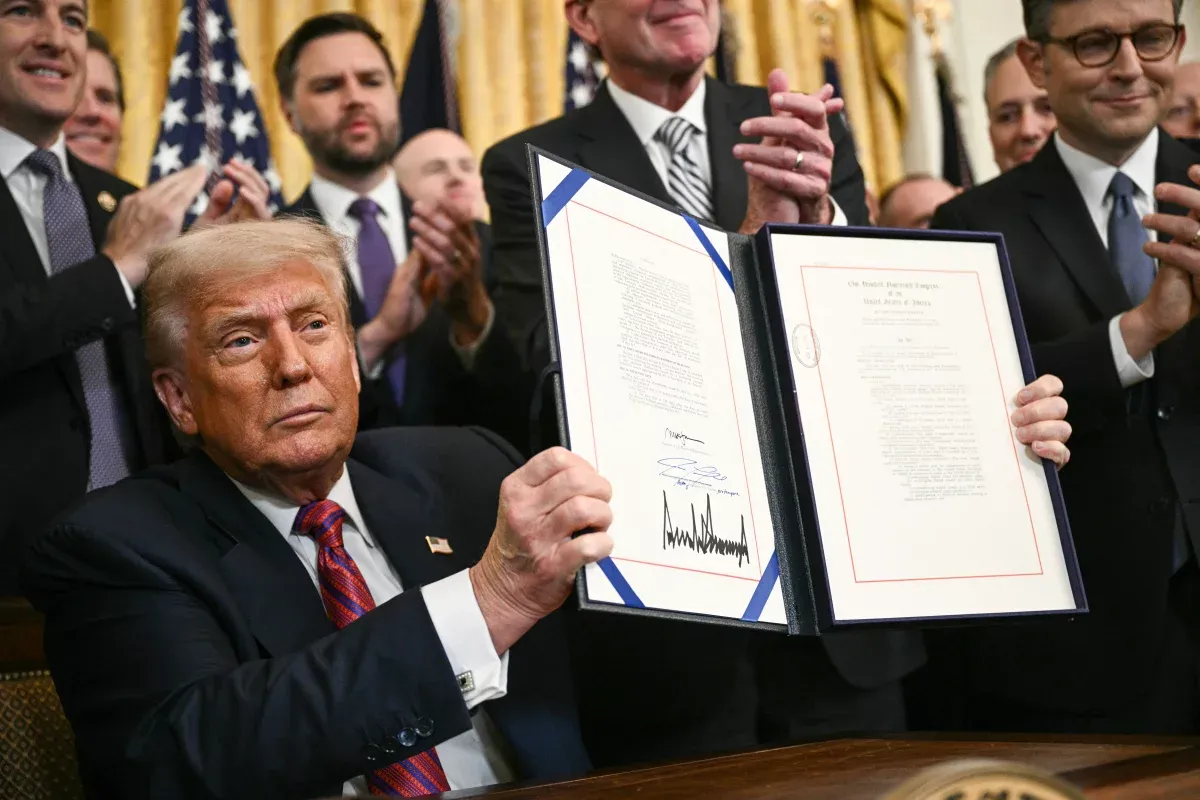

Signed on July 18, 2025, President Donald Trump formalized the Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins (GENIUS) Act, surrounded by executives from Coinbase, Kraken, Gemini, Tether, Circle, and others. He remarked that the law was “aptly named after me,” signaling his full embrace of the crypto industry’s evolution into mainstream finance.
This law is the first comprehensive federal framework for stablecoins, which are digital tokens pegged 1:1 to the U.S. dollar or low-risk Treasury assets. It codifies reserve standards, consumer rights, and regulatory obligations, aiming to legitimize stablecoins within the broader financial system.
What the GENIUS Act Does
Reserve Backing and Monthly Reporting
Issuers must fully back their tokens with liquid U.S. dollars, short-term Treasuries, demand deposits, or Federal Reserve balances. These assets must be held in segregated accounts and undergo third-party audits. Monthly public disclosures are required to promote transparency.
Consumer Protections
Stablecoin holders are given priority repayment in the event of an issuer’s insolvency. However, stablecoins are not covered by FDIC insurance. Instead, protections stem from asset segregation and reserve mandates.
Licensing and Issuer Eligibility
Only licensed institutions may issue payment stablecoins in the United States. This includes national banks, OCC-approved nonbank entities, and state-chartered firms under certified regulatory oversight. After a three-year transition, all non-compliant stablecoins will be prohibited from U.S. markets.
Federal-State Regulatory Structure
The law maintains a dual licensing system. While some issuers may operate under state regimes, they must also comply with federal requirements such as reserve transparency, consumer rights, and AML compliance. Federal preemption applies where conflicts arise.
Anti-Money Laundering and Sanctions Compliance
Stablecoin issuers must adhere to the Bank Secrecy Act and anti-terrorism regulations. Foreign entities serving U.S. customers must register with American regulators and meet equivalent compliance standards.
Legal Status Clarification
The Act legally distinguishes payment stablecoins from securities and commodities, addressing longstanding uncertainty. This offers clarity for developers, investors, and regulators.
Ethics Rules
Members of Congress and their immediate families are barred from profiting from stablecoin activity. However, this restriction does not extend to the president or their family, which has sparked criticism related to potential conflicts of interest.
Rulemaking Timeline
Regulators must propose rules within 180 days and finalize them within one year of the Act’s signing. Implementation will begin in late 2026, allowing institutions and the public to prepare for enforcement and compliance.
Study of Non-Payment Stablecoins
The law mandates an interagency study of other types of stablecoins, including algorithmic or commodity-backed versions. Findings are expected within one year and may form the basis of future legislation.
New Policy Elements
Cross-Border Enforcement
Foreign stablecoins marketed to U.S. users must register and follow U.S.-comparable regulations. Approved jurisdictions will be listed publicly by the Treasury Department.
Technology Interoperability
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) will collaborate with financial agencies to establish technical standards for interoperability. This provision aims to ensure consistent and compatible infrastructure across platforms.
Legislative Journey
| Stage | Date | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Senate vote | June 17, 2025 | Passed 68–30 |
| House vote | July 17, 2025 | Passed 308–122 |
| President’s signature | July 18, 2025 | Signed into law at White House |
The GENIUS Act concluded what lawmakers dubbed "Crypto Week"—a moment that also featured the passage of the Clarity Act and the Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act.
Market and Economic Impact
Market Reactions
Crypto markets rallied on the news. Bitcoin surpassed $123,000, Ethereum rose nearly 20 percent, and other major coins followed suit. Stock prices of Coinbase, Robinhood, and stablecoin infrastructure providers also spiked.
Boost to the Dollar and Treasuries
Stablecoins backed by U.S. Treasuries are expected to create long-term demand for government debt. Supporters argue this will reinforce the dollar's global reserve status. Treasury Secretary Bessent has called the Act “a structural win for U.S. financial influence.”
However, critics warn that mass stablecoin usage could create unintended volatility in Treasury markets. If stablecoin holders redeem en masse during periods of stress, rapid Treasury liquidations could disrupt yield curves or liquidity.
Traditional Finance Enters the Arena
Visa, Mastercard, Walmart, JPMorgan, and Meta have all indicated plans to explore or expand their stablecoin strategies. Analysts expect increased interest in tokenized payment systems across banking and retail.
Concerns and Criticism
Presidential Conflict of Interest
Ethics advocates argue that the law’s exemption for the president and their family is a major oversight. Trump and his sons reportedly have equity in World Liberty Financial, which issues the USD1 stablecoin. Opponents view this as a direct financial conflict.
Systemic Financial Risk
Economists worry that stablecoins could drain deposits from banks or trigger liquidity shocks in the Treasury market. A sudden redemption wave could resemble a digital bank run.
Inadequate Consumer Protection
Consumer advocates argue that while transparency has improved, protections like immediate redemption, fee clarity, and insurance remain weak. Without FDIC backing, users rely on the issuer's solvency and asset transparency.
Privacy and Surveillance
Civil liberties groups are concerned that enhanced AML enforcement may enable excessive surveillance. The law’s focus on compliance lacks clear privacy safeguards for users transacting in stablecoins.
Trump’s Crypto Pivot
Once skeptical of crypto, Trump has shifted significantly. Since his reelection in 2024, he has:
- Created a U.S. Strategic Bitcoin Reserve
- Directed the Treasury to establish a Digital Asset Stockpile
- Endorsed stablecoins as key to modernizing U.S. payments
- Released a meme coin ($TRUMP) and promoted private crypto development
This pivot is part of a broader national crypto strategy that prioritizes American leadership in blockchain and financial innovation.
What Happens Next?
- Agencies will finalize regulatory frameworks by July 2026
- Enforcement begins either by November 2026 or 120 days after final rule issuance, whichever is earlier
- The transition period for legacy stablecoins ends by 2028
- International coordination, including through the G20, is expected to influence the next round of rules
In addition, follow-up bills like the Clarity Act, which limits the SEC’s oversight of crypto tokens, are expected to pass later this year.
Broader Implications
Mainstreaming Stablecoins
With legal clarity in place, banks and corporations are likely to expand stablecoin adoption. Tokenized payments could soon become part of everyday commerce.
Geopolitical Effects
The GENIUS Act enhances the dollar’s global footprint by tying stablecoins directly to U.S. Treasuries. This could counter efforts by foreign central banks to de-dollarize global trade.
Technology and Market Structure
Interoperability requirements will shape future innovations in payments and settlement. Standardized APIs, custody requirements, and transparency rules may emerge as benchmarks for other jurisdictions.
Conclusion
The GENIUS Act marks a major milestone in the history of U.S. financial regulation. It brings structure to a fast-growing segment of digital assets while inviting scrutiny of political influence and financial risk. How the law is implemented over the next several years will determine whether the U.S. becomes the center of a responsible digital economy or the source of the next financial shock.
Its success will depend on vigilant rulemaking, fair enforcement, and an ongoing balance between innovation and stability.
References
















Comments ()