Understanding Crypto Scams and Malware: How to Protect Yourself

The cryptocurrency space has seen tremendous growth, but with it comes an increase in scams, malware, and sophisticated cyber threats. Many users have lost funds due to wallet drainers, phishing attacks, and compromised devices.
In this article, I will share my personal experience of being targeted by a malware attack, break down the most common crypto scams, and provide actionable steps to protect your assets from these threats.

1. My Experience: How I Got Scammed
I fell victim to a sophisticated malware attack involving a suspicious .exe file. The malware stole my browser data, crypto wallet credentials, and even manipulated authentication settings in my Gmail without requiring login credentials.
Despite fresh-installing Windows twice, the hacker still managed to change my authentication methods, raising concerns about persistent malware, linked compromised accounts, or even hardware-level keyloggers.
Consulting cybersecurity experts made me realize that even hidden threats can survive basic security measures. This experience taught me that advanced protection is crucial to safeguard crypto assets.
2. Types of Crypto Scams and Malware
A. Common Crypto Scams
- Phishing Attacks
Fake websites or pop-ups trick users into entering their seed phrases.
Example: Fake MetaMask login screens.
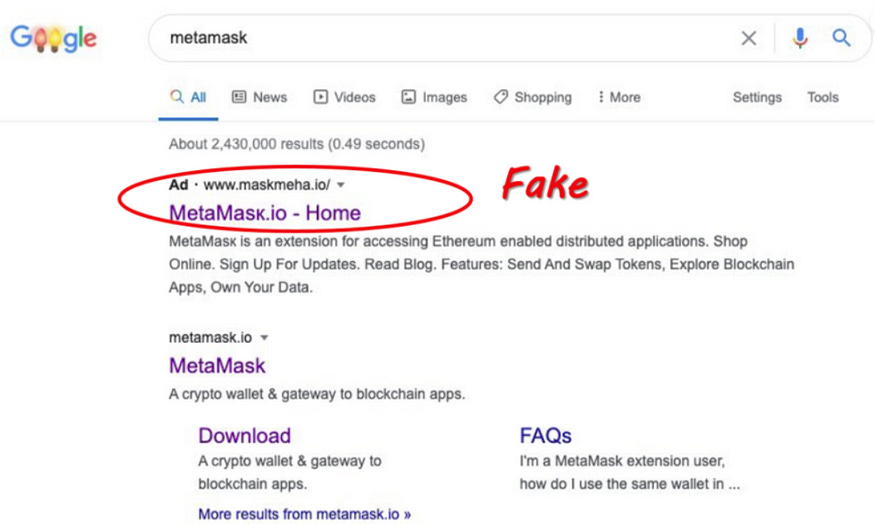
- Drainer Websites
What are drainers?
Malicious scripts embedded in fake airdrop sites, NFT minting pages, or “free token” offers. Once you sign a transaction, the drainer empties your wallet.
- How they work:
- Use social engineering to trick users into approving malicious smart contracts (e.g., fake token approvals).
- Deploy bots to front-run transactions, making recovery impossible even if you notice the theft immediately.
- Example: Toolkits sold on dark web forums to scammers.
3. Smart Contract Exploits
Malicious contracts that drain wallets upon interaction.
4. Rug Pulls & Pump-and-Dump Schemes
Fraudulent projects lure investors before disappearing with funds.
5. Giveaway Scams
Scammers impersonate famous people (e.g., Elon Musk) and promise to double your crypto.
6. Fake Customer Support Scams
Fraudsters pretending to be from Binance, MetaMask, or Trust Wallet.
B. Malware Targeting Crypto Users
- Clipboard Hijackers
Replaces copied wallet addresses with the hacker’s address. - Keyloggers
Tracks keystrokes to steal passwords and private keys. - Remote Access Trojans (RATs)
Grants hackers' full control over the victim’s device. - Browser Hijacking Malware
Extracts stored passwords and session cookies. - DNS and Router Hijacking
Redirects users to fake websites even if they type the correct URL.
Malware from Executable Files (.exe)
How it works:
- Attackers disguise malware as legitimate software (e.g., wallet apps, trading tools, or game mods).
- Once the .exe file is executed, the malware gains full control of your system, stealing sensitive data like wallet credentials, seed phrases, and browser cookies.
- In my case, I downloaded a file thinking it was a legitimate application, but it turned out to be suspicious .exe file malware. It hijacked my browser, stole my crypto wallet credentials, and even manipulated my Gmail authentication settings all without requiring login credentials.
Common sources:
- Pirated software or cracked games.
- Fake wallet apps or trading tools from untrusted websites.
- Email attachments or downloads from suspicious links.
How to protect yourself:
- Never download .exe files from untrusted sources: Only use official websites or app stores.
- Verify file integrity: Check the SHA-256 hash of the file against the official source.
- Use a sandbox: Run suspicious files in a virtual machine or sandbox environment (e.g., Sandboxie) to isolate them from your main system.
- Scan files before opening: Use antivirus tools like Malwarebytes or VirusTotal to scan downloads.
- Disable auto-run for external devices: Prevent malware from spreading via USB drives or external hard drives.
What to do if infected:
- Disconnect from the internet immediately to prevent further data leaks.
- Boot into Safe Mode and run a full system scan using trusted antivirus software.
- If the malware persists, wipe your system and reinstall the operating system from a clean backup.
- Change all passwords and revoke wallet approvals from a clean device.
3. Essential Tools & Extensions for Crypto Security
A. Browser Security Tools
- MetaMask + Hardware Wallet (Ledger/Trezor)
Why? MetaMask alone is vulnerable but pairing it with a hardware wallet prevents key theft. - uBlock Origin
Why? Blocks malicious ads and phishing sites. - Cryptonite by MetaCert
Why? Flags phishing sites and highlights trusted crypto websites. - Wallet Guard
Why? Detects wallet-draining dApps before they execute transactions. - HTTPS Everywhere
Why? Prevents access to fake sites using HTTP instead of HTTPS.
B. Anti-Malware & System Protection
- Malwarebytes / Emsisoft Anti-Malware
Why? Detects clipboard hijackers, keyloggers, and RATs.

- GlassWire Firewall
Why? Monitors outgoing network traffic for suspicious activity. - Windows Defender (With Controlled Folder Access Enabled)
Why? Blocks unauthorized modifications to sensitive files.
4. Wallet Management Strategies
A. Segregate Wallets by Risk Profile
- Cold Wallet
- Use: Long-term storage of large holdings.
- Setup: Hardware wallet (Ledger/Trezor) + dedicated browser profile with no extensions.
- Hot Wallet
- Use: Daily transactions (small amounts).
- Setup: Software wallet (MetaMask) on a separate browser (e.g., Firefox) with strict security extensions.
- Airdrop Wallet
- Use: Interacting with new projects, claiming tokens.
- Setup: Disposable wallet (e.g., new MetaMask instance) with no funds beyond what’s needed for gas.
- Risky Wallet
- Use: Testing unknown dApps, participating in meme coins.
- Setup: Burner wallet (e.g., Coinbase Wallet mobile app) isolated from main devices.
B. Advanced Security Practices
- Browser Profile Separation
- Use Chrome profiles or separate browsers (Brave, Firefox) for each wallet type to prevent cross-contamination.
- Example: Use Brave for airdrops, Chrome with hardware wallet for cold storage.
- Spending Limits
- Set transaction limits on wallets (e.g., via Argent Wallet) to minimize losses if compromised.
- Wallet Monitoring
- Use DeBank or Zerion to track approvals and balances across wallets without exposing keys.
5. What to Do If Your Wallet or System Is Compromised
A. Immediate Actions
- Disconnect from the Internet: Prevent further data leaks or remote access.
- Revoke Approvals: Use Revoke.cash or Etherscan’s Token Approval Tool.
- Transfer Remaining Funds: Send assets to a new wallet (ideally a hardware wallet) from a clean device.
- Wipe and Reinstall OS: Format the infected device and restore from a pre-attack backup.
B. Managing a Drained Wallet
- Do NOT Reuse the Wallet: Assume private keys are compromised.
- Test for Residual Malware:
- Send a small amount to the drained wallet. If it disappears immediately, then a bot is active to drain your wallet.
- Use Malwarebytes or HitmanPro to scan for keyloggers.
- Blacklist the Address: Mark it as compromised in your records to avoid accidental reuse.
C. Flash Bots and Recovery
- Flash Bots:
- Tools like Flashbots Protect can front-run drainer bots but require advanced technical knowledge.
- Not user-friendly for beginners — consult a blockchain developer if funds are critical.
6. Security Maintenance: Preventing Future Attacks
A. Wallet & Smart Contract Security
- Revoke Token Approvals
Use Revoke.cash or Etherscan Token Approval Checker to remove wallet permissions given to suspicious smart contracts.
Why? Many wallet-draining scams rely on infinite approvals, allowing hackers to access funds anytime.

- Always Open Official Sign-In Links
Visit exchanges and wallets directly from official sources rather than clicking links from emails or messages.
Why? Fake login pages look identical to real ones and steal credentials. - Test Contracts Before Interacting:
Use testnets or tools like Tenderly to simulate transactions. - Verify Contract Addresses:
Cross-check on Etherscan, CoinGecko, or the project’s official Telegram/Discord.
B. Account & Device Security
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Prefer hardware-based 2FA (YubiKey) over SMS-based authentication.
Why? SIM swapping attacks can compromise SMS-based 2FA. - Use a Dedicated Crypto Device
Consider using a separate phone or PC for crypto transactions.
Why? Limits exposure to malware from daily browsing. - Regularly Clear Browser Cache & Cookies
Why? Stored cookies can be used to hijack login sessions. - Never Store Passwords in Browsers
Use a secure password manager instead.
Why? Malware can extract saved passwords. - Air-Gapped Signing:
For cold wallets, sign transactions offline using tools like Electrum (for Bitcoin) or offline MetaMask.
C. Network & Router Security
- Change Router Login Credentials
Why? Many routers have default admin credentials, making them easy targets. - Use a VPN for Crypto Transactions
Why? Prevents ISP tracking and potential DNS hijacking attacks. - Manually Set Secure DNS (e.g., Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 or Google 8.8.8.8)
Why? Blocks malicious redirects from compromised routers.
D. Education and Vigilance
- Follow Security Experts:
Track updates from @zachxbt, @tayvano_, and SlowMist. - Verify Everything:
Assume 90% of DMs, “support agents,” and too-good-to-be-true offers are scams.
7. Conclusion
Crypto scams and malware are constantly evolving, but vigilance, security tools, and regular maintenance can significantly reduce risks. My experience highlights how even advanced users can be targeted, and I hope this guide helps others stay protected.
Key Takeaways:
✅ Use a hardware wallet to prevent key theft.
✅ Segregate wallets by purpose (cold, hot, airdrop, risky) and use separate browser profiles.
✅ Revoke permissions regularly using Revoke.cash.
✅ Enable 2FA with a hardware key (avoid SMS 2FA).
✅ Use browser security extensions to block phishing sites.
✅ Change router login details & use a VPN to prevent hijacking.
✅ Assume drainer bots will win never approve unlimited token allowances.
✅ If compromised, revoke approvals immediately and migrate funds to a new wallet.
By adopting these security practices, you can keep your funds safe and prevent future attacks. Stay alert, double-check every transaction, and never share your seed phrase with anyone!
If you’ve encountered similar scams, share your experience to help raise awareness in the crypto community!



Comments ()