EigenLayer & AVS Explained: How Restaking is Changing Blockchain Security

Introduction to EigenLayer
What is EigenLayer?
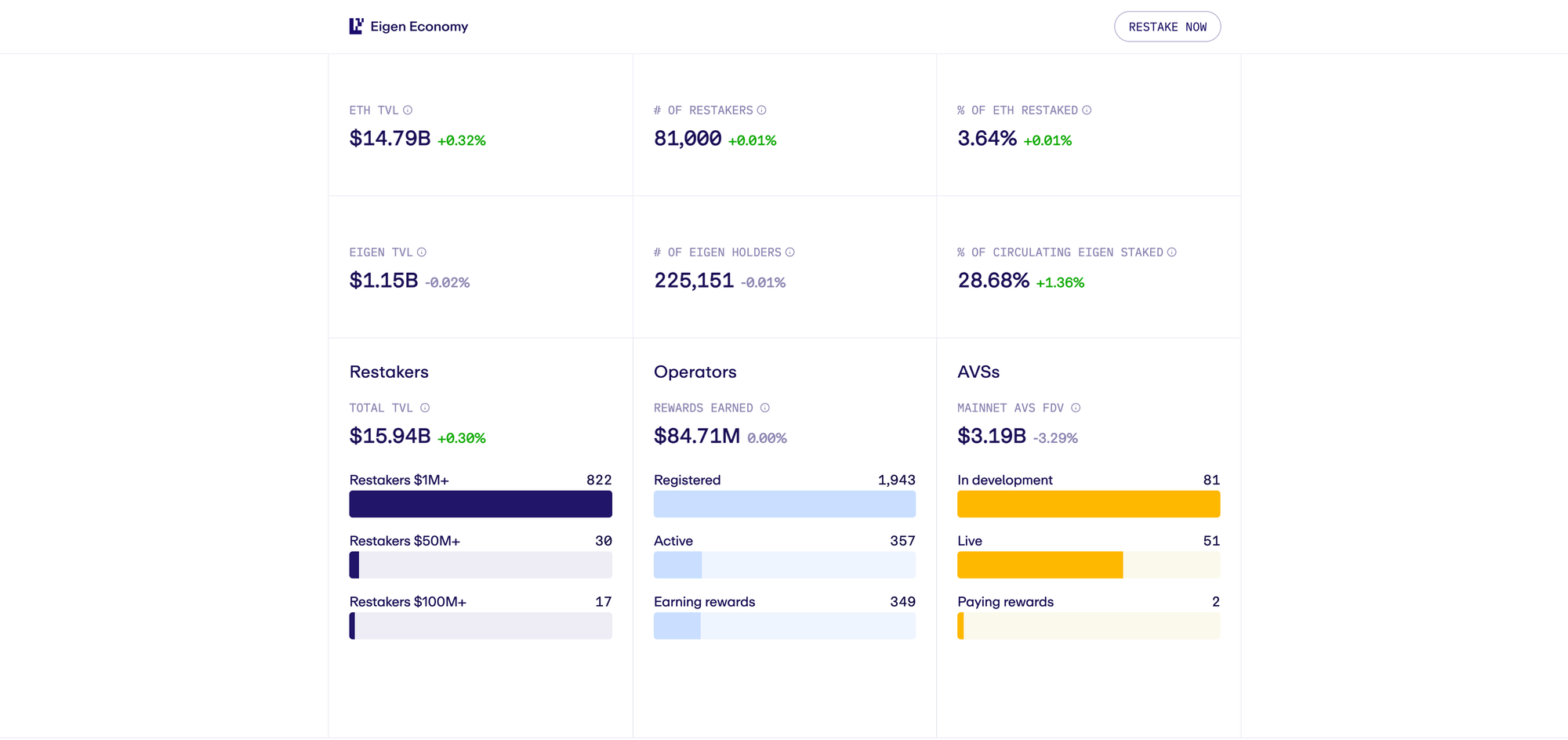
EigenLayer is an innovative protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain that enhances blockchain security and scalability through a concept known as restaking. It allows ETH stakers to reuse their staked tokens, including liquid staking tokens, to secure various protocols beyond Ethereum. By leveraging restaked ETH, EigenLayer creates a shared security network, reducing operational costs for developers and fostering innovation across decentralized ecosystems.
The protocol supports Actively Validated Services (AVS) like data availability layers, cross-chain bridges, and oracles, which play a pivotal role in expanding Ethereum’s security model and enabling modular blockchain applications.
Why Does EigenLayer Matter?
EigenLayer addresses critical limitations in Ethereum’s security model, where validation services are traditionally tied to a single network. By introducing EigenLayer Restaking, the protocol enables ETH stakers to secure multiple services simultaneously while earning additional rewards. This innovative approach promotes capital efficiency and reduces barriers for node operators and developers.
Key Contributions:
- Expands Ethereum’s security model by decentralizing validation services across various protocols.
- Facilitates the growth of new protocols by providing an own trust network without requiring developers to build it from scratch.
- Increases the total value locked (TVL) in Ethereum-based systems.
What Does EigenLayer Do?
Enhancing Blockchain Security Through Restaking
EigenLayer’s core innovation is native restaking, a process that allows ETH tokens already staked on the Ethereum blockchain to secure additional protocols. This groundbreaking approach enables validators and stakers to extend their roles without requiring extra hardware or consuming additional energy, making blockchain security more efficient and scalable.
How EigenLayer works:
- Restaking Assets: Validators can restake ETH or liquid staking tokens (like those from Lido or Rocket Pool) into the EigenLayer protocol.
- Securing Actively Validated Services (AVS): Restaked assets are pledged to AVS, including:
- Data Availability Layers: Ensuring secure data storage for Layer 2 rollups and modular blockchains.
- Cross-Chain Messaging Protocols: Facilitating seamless communication and transfers between blockchains.
- Oracles: Providing reliable, decentralized price feeds for DeFi platforms and dex aggregators.
- Reward Mechanism: Validators earn additional yield from protocol fees while maintaining their primary roles on the Ethereum network. Yield distribution mechanisms are subject to EigenLayer’s ongoing protocol development.
Benefits of Restaking with EigenLayer:
- Capital Efficiency:
- Staked tokens are utilized across multiple networks, maximizing returns without additional investments in hardware or energy.
- Example: A validator staking 32 ETH on Ethereum can also secure an MEV management protocol through EigenLayer, earning rewards from both.
- Additional Rewards:
- Validators earn fees and incentives from the protocols they support.
- Example: A validator supporting a cross-chain messaging protocol and a data availability layer can earn protocol fees in ETH or other tokens like EIGEN.
- Reduced Redundancy:
- Eliminates the need for separate validator infrastructures for each protocol, reducing costs and complexity for new projects.
- Example: A startup launching a decentralized gaming platform avoids the need to build a standalone validator network by leveraging EigenLayer’s shared security.
How Does EigenLayer Work?
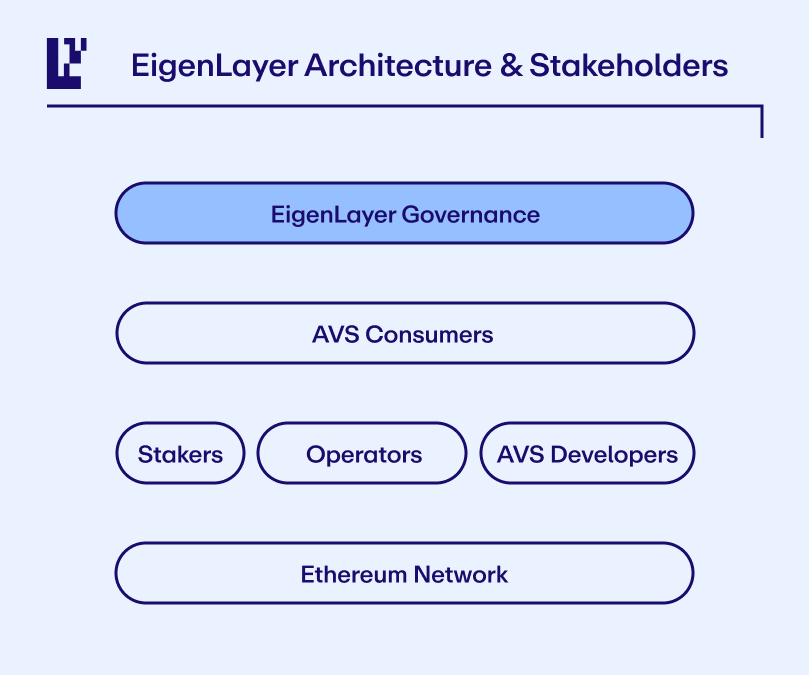
Restaking and Its Role in EigenLayer
EigenLayer enables native restaking, allowing staked tokens to secure multiple protocols simultaneously. This process is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and integrates seamlessly with other blockchain solutions, enhancing scalability and efficiency across networks.
- Validators and Node Operators: By opting into EigenLayer, validators expand their roles to support additional protocols. Robust slashing mechanisms ensure accountability for any attributable faults, preserving the integrity of the system.
- Developer Efficiency: EigenLayer reduces operational costs for developers by providing shared infrastructure and enabling scalable modular services, allowing them to focus on innovation.
Examples of EigenLayer Applications
- MEV Management: EigenLayer helps mitigate Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) risks, promoting fairer and more equitable transaction processing.
- Oracles and Price Feeds: By leveraging EigenLayer, decentralized systems gain access to trustworthy and efficient data provisioning for price feeds and other critical metrics.
EigenLayer AVS (Actively Validated Services)
What Are AVS?
Actively Validated Services (AVS) are modular services that leverage EigenLayer’s restaking tokens for enhanced security. These services utilize EigenLayer’s shared infrastructure, enabling cost-effective scaling and seamless interoperability across networks.
Examples of AVS:
- Oracles: Provide reliable data feeds for dApps and dex aggregators.
- Data Availability Layers: Verify and store block data for rollups, enhancing scalability.
- Cross-Chain Bridges: Facilitate secure asset transfers across blockchains.
EigenLayer Token: Current and Future Potential
What is EigenLayer Token(EIGEN)?
EigenLayer has officially launched its native token, EIGEN, to enhance its ecosystem. As of October 1, 2024, the token became transferable, marking a significant milestone for the protocol. EIGEN serves as a complementary asset to Ethereum's restaking capabilities, addressing security, governance, and incentivization within the EigenLayer ecosystem.
Key Features of the EIGEN Token
- Governance: EIGEN token holders can participate in protocol upgrades and critical operational decisions, ensuring community-driven development.
- Incentives: Validators and participants earn EIGEN rewards for securing Actively Validated Services (AVS) such as data availability layers, cross-chain messaging protocols, and oracles.
- Intersubjective Fault Mitigation: The token incorporates mechanisms like intersubjective forking, enabling disputes over misbehaviors to be resolved without disrupting Ethereum's mainnet consensus.
- Liquidity: EIGEN facilitates liquidity for services and applications within the EigenLayer ecosystem, stabilizing price ranges for AVS markets.
EIGEN Token Adoption Metrics
- Total Supply: As of September 30, 2024, approximately 158,774,855 EIGEN tokens have been claimed.
- Community Participation: Over 4.1 million ETH has been restaked on EigenLayer, reflecting strong community engagement and confidence in the protocol.
Strategic Enhancements with EIGEN
EigenLayer has formed partnerships to amplify the utility of the EIGEN token:
- AI Integration with Ritual: Collaboration to develop Actively Validated Services (AVS) integrating AI for advanced decentralized applications.
- Marketplace Development with Nethermind: Creation of a decentralized trust marketplace, combining Ethereum's security with EigenLayer's modular scalability.
The EIGEN token has transitioned from speculation to reality, playing a pivotal role in scaling and securing EigenLayer’s ecosystem while fostering innovation and collaboration across decentralized platforms.
Challenges and Risks of EigenLayer
1. Complexity for Validators and Developers
- Challenge: Adopting EigenLayer’s restaking model involves a steep learning curve, especially for new participants.
- Solution: EigenLayer is actively improving onboarding resources and releasing comprehensive documentation to assist developers and validators.
2. EigenLayer's Security Risks
- Challenge: Over-reliance on restaked ETH may increase risks, such as slashing penalties for validator misconduct. Slashing mechanisms in EigenLayer hold validators accountable for network misbehavior, such as failing to secure AVS or colluding in malicious activity. These mechanisms, inherited from Ethereum’s proof-of-stake model, ensure that restaked ETH remains a reliable security asset. For instance, a validator providing faulty data for an oracle service could face slashing penalties proportionate to their restaked assets, deterring misconduct.
- Solution: Robust slashing mechanisms and transparent governance are in place to minimize these risks and maintain trust.
3. EigenLayer's Competitors
While Optimism and zkSync focus primarily on Layer 2 scaling, EigenLayer’s unique contribution lies in creating a decentralized security marketplace through restaking. Unlike Polygon or Cosmos SDK platforms, which emphasize interoperability, EigenLayer prioritizes modular scalability by enabling Actively Validated Services (AVS) like oracles, cross-chain bridges, and data availability layers to leverage shared Ethereum security.
Getting Started with EigenLayer
For Validators and Stakers
- Choose Reliable Operators: Partner with trusted EigenLayer Operators to ensure your staked tokens are secure.
- Monitor Metrics: Regularly track the total value locked (TVL), rewards, and slashing risks associated with your staked assets.
- Maximize Yield Opportunities: Participate in validation services to earn additional rewards from restaking your ETH or liquid staking tokens.
For Developers
- Access Comprehensive Resources: Begin by exploring the EigenLayer Whitepaper and official documentation to understand the protocol’s architecture.
- Leverage Actively Validated Services (AVS): Integrate AVS like data availability layers, oracles, and cross-chain messaging protocols to build scalable and secure decentralized services.
- Collaborate with the Ecosystem: Engage with the Eigen Foundation and the broader community to refine your protocol, contribute innovations, and align with the evolving EigenLayer ecosystem.
Conclusion
EigenLayer is transforming the blockchain landscape by introducing restaking and Actively Validated Services (AVS), with potential future enhancements like a native token under community discussion. This modular protocol not only enhances Ethereum's security model but also fosters innovation by reducing entry barriers for developers and validators.
Early participation in EigenLayer offers exciting opportunities, including potential airdrops for active contributors. Whether you're a validator seeking additional rewards or a developer building scalable decentralized services, EigenLayer provides a forward-thinking ecosystem to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving blockchain space.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is EigenLayer?
EigenLayer is a modular protocol on Ethereum that introduces restaking, allowing ETH stakers to secure multiple protocols simultaneously, enhancing security and scalability.
How does EigenLayer's restaking work?
Restaking allows staked ETH or liquid staking tokens to be reused to secure additional protocols like data availability layers, oracles, and cross-chain bridges, earning extra rewards.
What are EigenLayer staking rewards?
EigenLayer staking rewards come from securing Actively Validated Services (AVS), allowing validators and stakers to earn additional yield on top of their Ethereum staking rewards. Rewards typically include ETH-based fees or protocol-native tokens (such as EIGEN) distributed by the AVS they secure. The exact reward structure depends on network participation, AVS demand, and protocol fees.
What are Actively Validated Services (AVS) in EigenLayer?
AVS are modular services like oracles, data availability layers, and cross-chain bridges that leverage EigenLayer’s restaking tokens for enhanced security and scalability.
What risks are associated with EigenLayer?
EigenLayer introduces risks such as slashing penalties, where validators can lose staked ETH if they fail to secure Actively Validated Services (AVS) or engage in malicious behavior. Additionally, smart contract vulnerabilities and potential governance centralization pose risks if not properly managed. Since restaking spreads security across multiple protocols, a failure in one AVS could have cascading effects on staked assets.



Comments ()