What are Consensus Mechanisms in blockchain and cryptocurrency?
Choosing Trust Without a Middleman: Web3’s Evolving Consensus Models.
In the world of Web3, blockchains are designed to operate without a central authority. But without a middleman, how can thousands of distributed nodes agree on a single version of the truth?
That’s where consensus mechanisms come in.
🧠 What Are Consensus Mechanisms in Web3?
A consensus mechanism is the method by which a blockchains network agrees on the validity of transactions and the current state of the ledger. It ensures that:
- All participants (nodes) agree on the same data (consensus)
- The network remains secure and tamper-proof
- There is fair and trustless participation
In Web3, consensus is critical because it enables decentralized applications (dApps), decentralized finance (DeFi), non-custodial wallets, NFTs, and more to function without relying on a single trusted party.
The two most well-known consensus mechanisms are:
- Proof of Stake (PoS) — Used by Ethereum; validators stake crypto to secure the network.
- Proof of Work (PoW) — Used by Bitcoin; requires computational work to validate blocks.
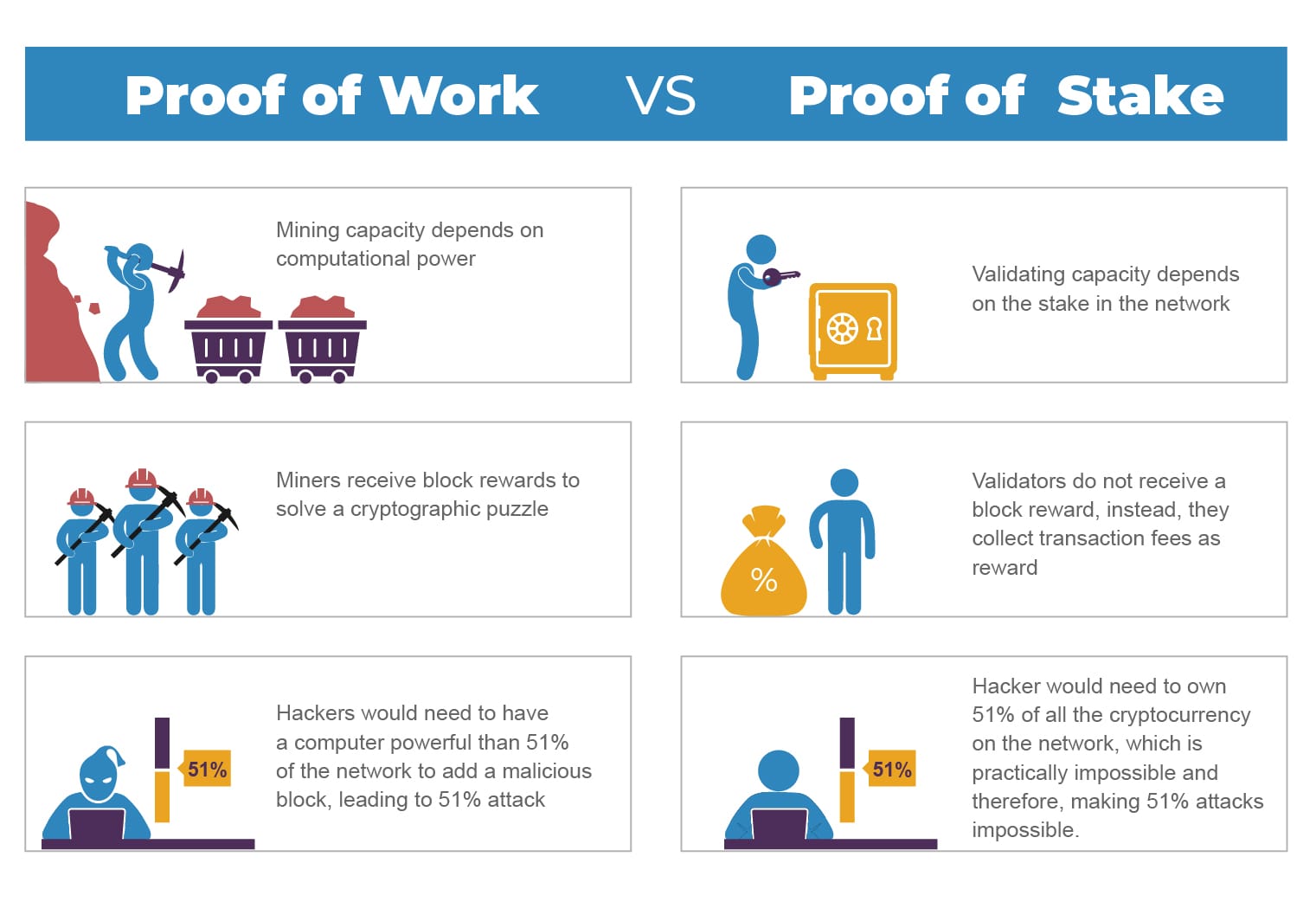
But in 2025, the landscape has evolved far beyond these.
Let’s explore the other major consensus models, each designed for specific trade-offs like energy efficiency, speed, decentralization, and scalability.
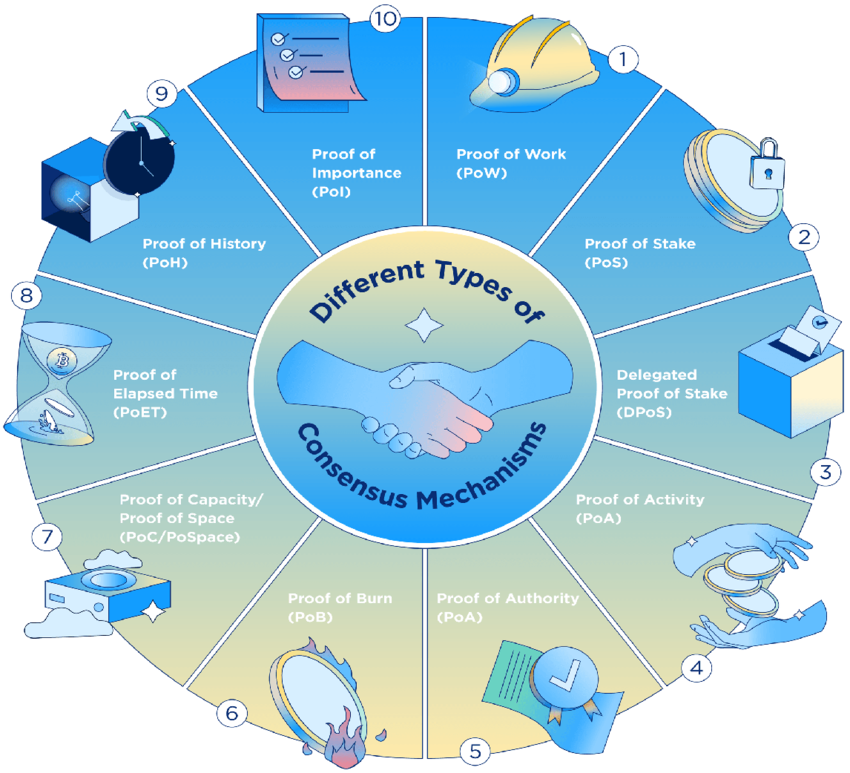
Consensus Mechanisms and Their “Proofs”
Each mechanism is centered around a type of “proof” which is a cryptographic or economic guarantee that a node has earned the right to propose or validate the next block. Below are the top 10 alternative proofs in use across modern blockchains:
1. ✅ Proof of Authority (PoA)
- How It Works: validators are pre-approved based on their identity or reputation.
- Best For: Enterprise blockchains, private networks.
- Used By: VeChain, Binance Smart Chain (some configurations).
- Pros: Fast, low energy.
- Cons: Centralized; depends on trust in validators.
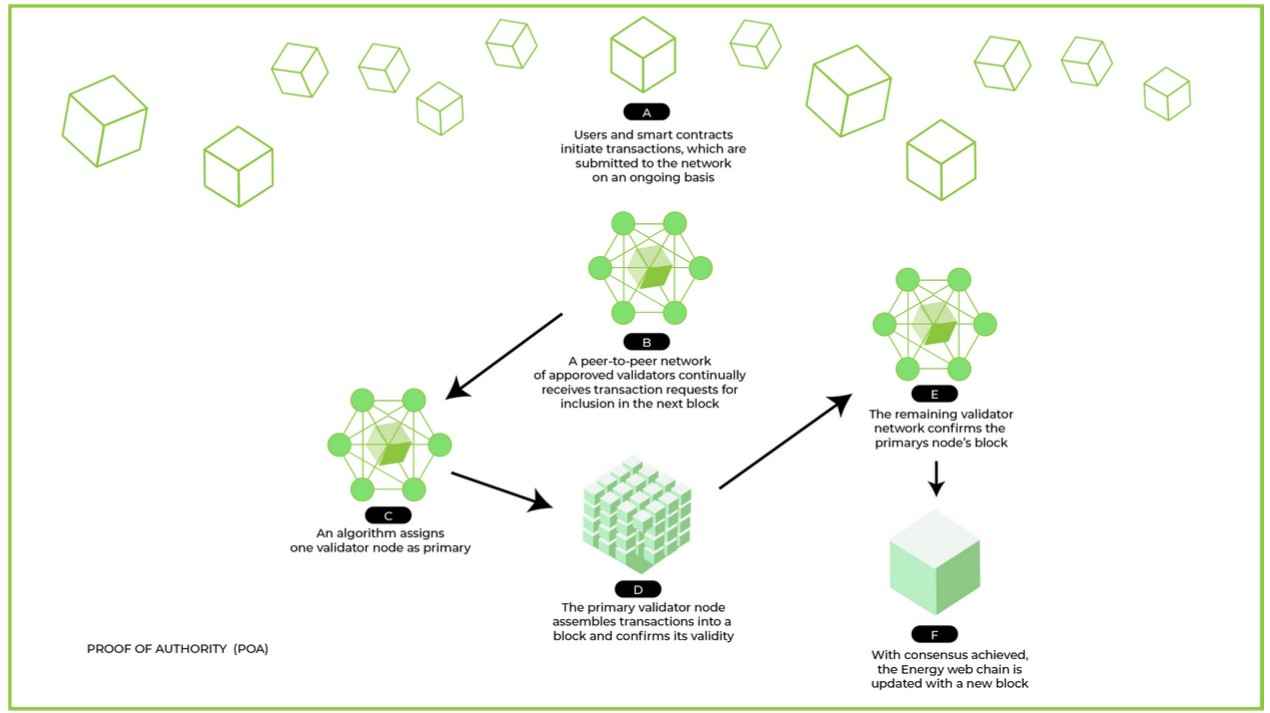
🧠 Think of a company where only trusted managers can approve decisions.
2. 🗳️ Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- How It Works: Token holders vote for a limited set of delegates to produce blocks.
- Best For: High-throughput dApps, games, DeFi.
- Used By: EOS, Tron, BitShares.
- Pros: Scalable, energy-efficient.
- Cons: Risk of centralization if voting is concentrated.
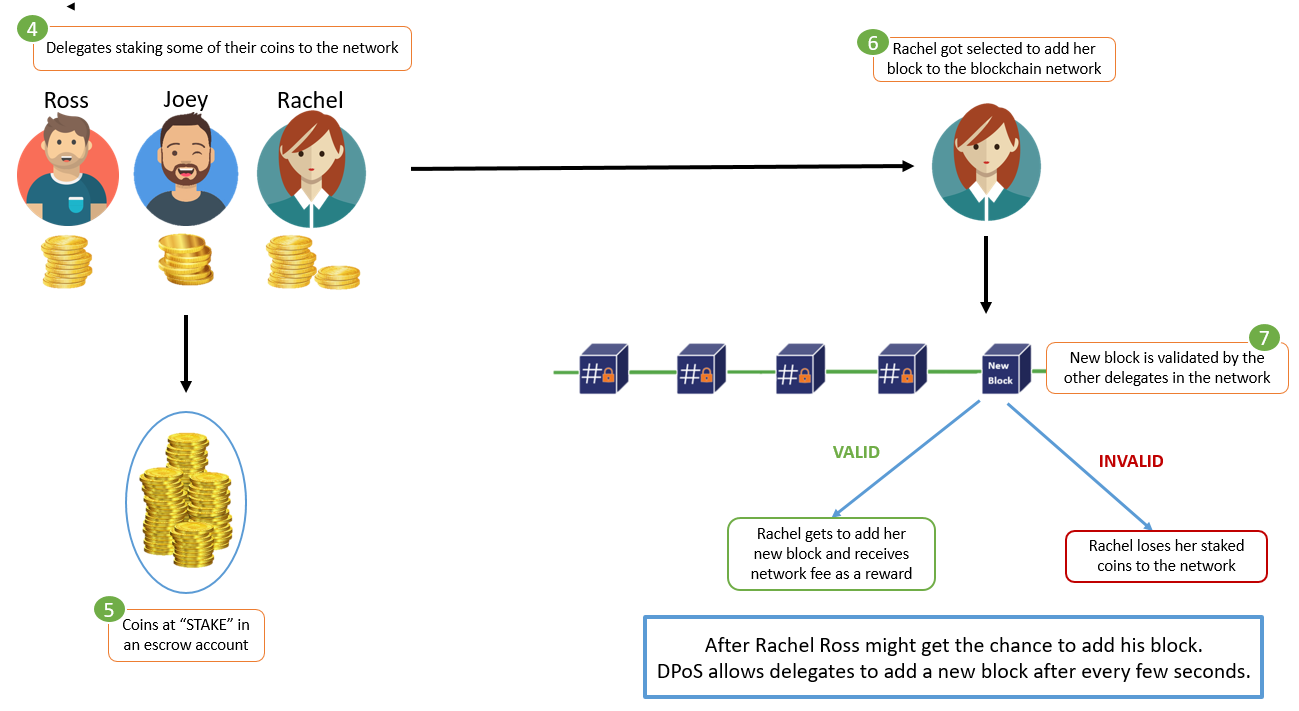
🧠 It’s like electing a parliament to represent thousands of citizens.
3. ⏱️ Proof of History (PoH)
- How It Works: Uses a cryptographic clock to timestamp events in order before consensus.
- Best For: Ultra-fast transactions, DeFi, NFT mints.
- Used By: Solana.
- Pros: Low latency, thousands of TPS.
- Cons: Requires precise clocking and custom architecture.
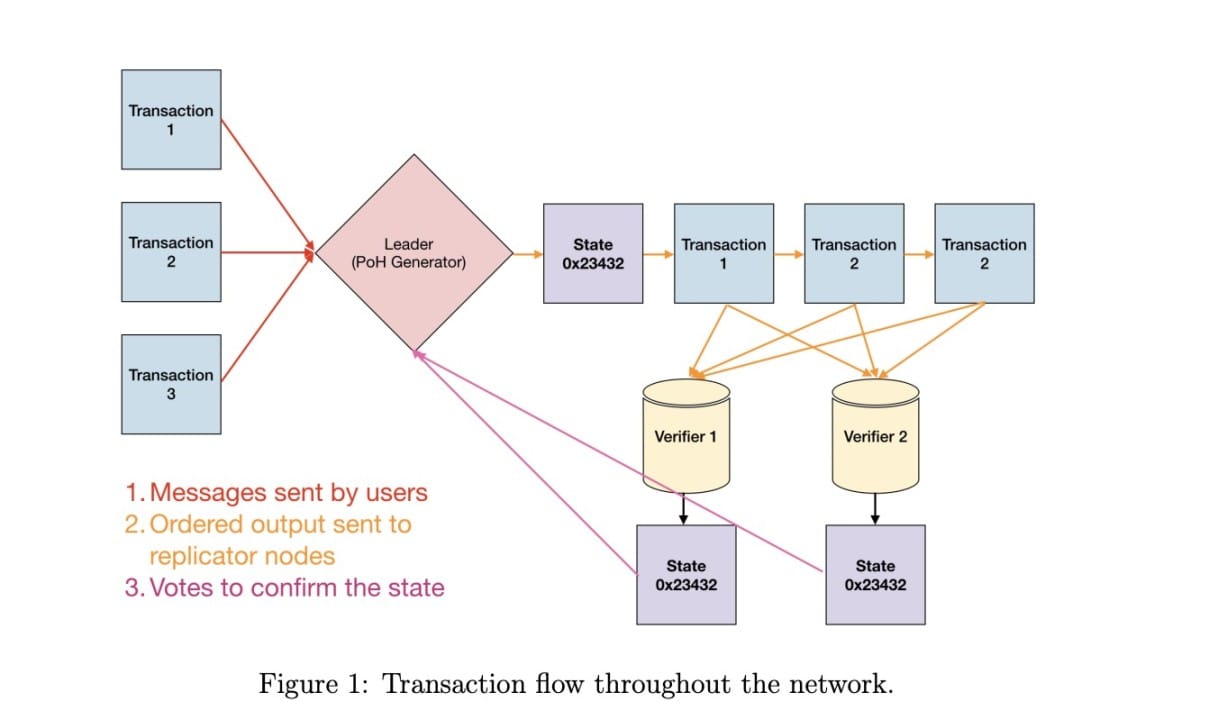
🧠 It’s like recording every step on camera to prove the sequence of events.
4. 💽 Proof of Space (PoSpace) / Proof of Capacity (PoC)
- How It Works: Miners allocate hard drive space to store solutions for cryptographic puzzles.
- Best For: Sustainable networks, energy-conscious users.
- Used By: Chia Network.
- Pros: Energy-efficient; eco-friendly.
- Cons: Encourages large storage farms; hardware access matters.
🧠 You win not by working harder, but by owning more digital “land.”
5. 🔥 Proof of Burn (PoB)
- How It Works: Participants destroy (burn) tokens to earn validation rights.
- Best For: Long-term commitment-focused networks.
- Used By: Slimcoin, Counterparty.
- Pros: Aligns incentives with network health.
- Cons: Wastes resources; hard to grasp for new users.
🧠 Imagine buying a license by burning money. Risky, but signals you’re serious.
6. ⏳ Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)
- How It Works: Nodes wait for a randomly assigned time; shortest timer wins the block.
- Best For: Consortiums, enterprise use.
- Used By: Hyperledger Sawtooth.
- Pros: Fair, low power usage.
- Cons: Requires trusted hardware (e.g., Intel SGX).
🧠 Like drawing straws—random, but verifiable via hardware.
7. ⚡ Proof of Activity (PoA)
- How It Works: Combines PoW and PoS where miners create blocks (PoW), then validators (PoS) confirm them.
- Best For: Security-focused chains.
- Used By: Decred.
- Pros: Balances security and efficiency.
- Cons: Still partially relies on energy-intensive PoW.
🧠 A two-step process—first a miner finds a block, then stakers vote on it.
8. 🧮 Proof of Importance (PoI)
- How It Works: Nodes are ranked based on stake, transaction behavior, and network contribution.
- Best For: Community-driven chains.
- Used By: NEM / Symbol.
- Pros: Encourages active participation.
- Cons: Complex scoring system; risk of gaming the model.
🧠 You’re rewarded not just for what you hold, but for what you do in the network.
9. 🌟 Proof of Reputation (PoR)
- How It Works: Validator selection depends on reputation scores, not stake or work.
- Best For: DAOs, permissioned networks.
- Used By: GoChain, some experimental DeFi DAOs.
- Pros: Promotes honesty and trustworthiness.
- Cons: Reputation metrics can be gamed or biased.
🧠 A blockchain that works like a five-star Uber driver system.
10. 📦 Proof of Space-Time (PoST)
- How It Works: validators prove they’ve maintained storage over time.
- Best For: Sustainable and decentralized storage networks.
- Used By: Spacemesh.
- Pros: Low energy, long-term incentive.
- Cons: Still experimental; adoption and performance vary.
🧠 Not just renting space but also proving you’ve kept it online long enough to earn trust.
🧭 Which “Proof” Is Right for What?
| Use Case | Recommended Consensus |
|---|---|
| Enterprise & Consortium Chains | PoA, PoET |
| Sustainable or Eco-Friendly Projects | PoSpace, PoST |
| High-TPS DeFi / NFT platforms | PoH, DPoS |
| Security-Heavy Networks | PoA (activity), hybrid PoW/PoS |
| Community Participation & Governance | PoI, PoR |
| Long-Term Commitment Models | PoB, PoST |
📌 Conclusion: Why Consensus Matters More Than Ever
In the multi-chain world of 2025, consensus is no longer just a technical protocol. It’s a design choice that shapes everything from transaction speed to decentralization, from validator incentives to energy use.
As Web3 expands into new sectors like AI, IoT, gaming, and real-world asset tokenization, choosing the right proof-of-mechanism becomes as important as the blockchain’s codebase itself.
Consensus is the foundation for trust, and in a trustless world, it’s everything.



Comments ()