What Are Wrapped Tokens? The Key to Building Bridges Between Blockchains

The world of cryptocurrency faces a major issue: different blockchains cannot communicate directly with one another. You can’t use Bitcoin on the Ethereum network, and Ethereum is not a native asset on the BNB Chain.
This is where Wrapped Tokens come into play. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of wrapped tokens from the ground up, explain how they work using simple examples, and discuss their importance within the crypto ecosystem.
What Is a Wrapped Token?
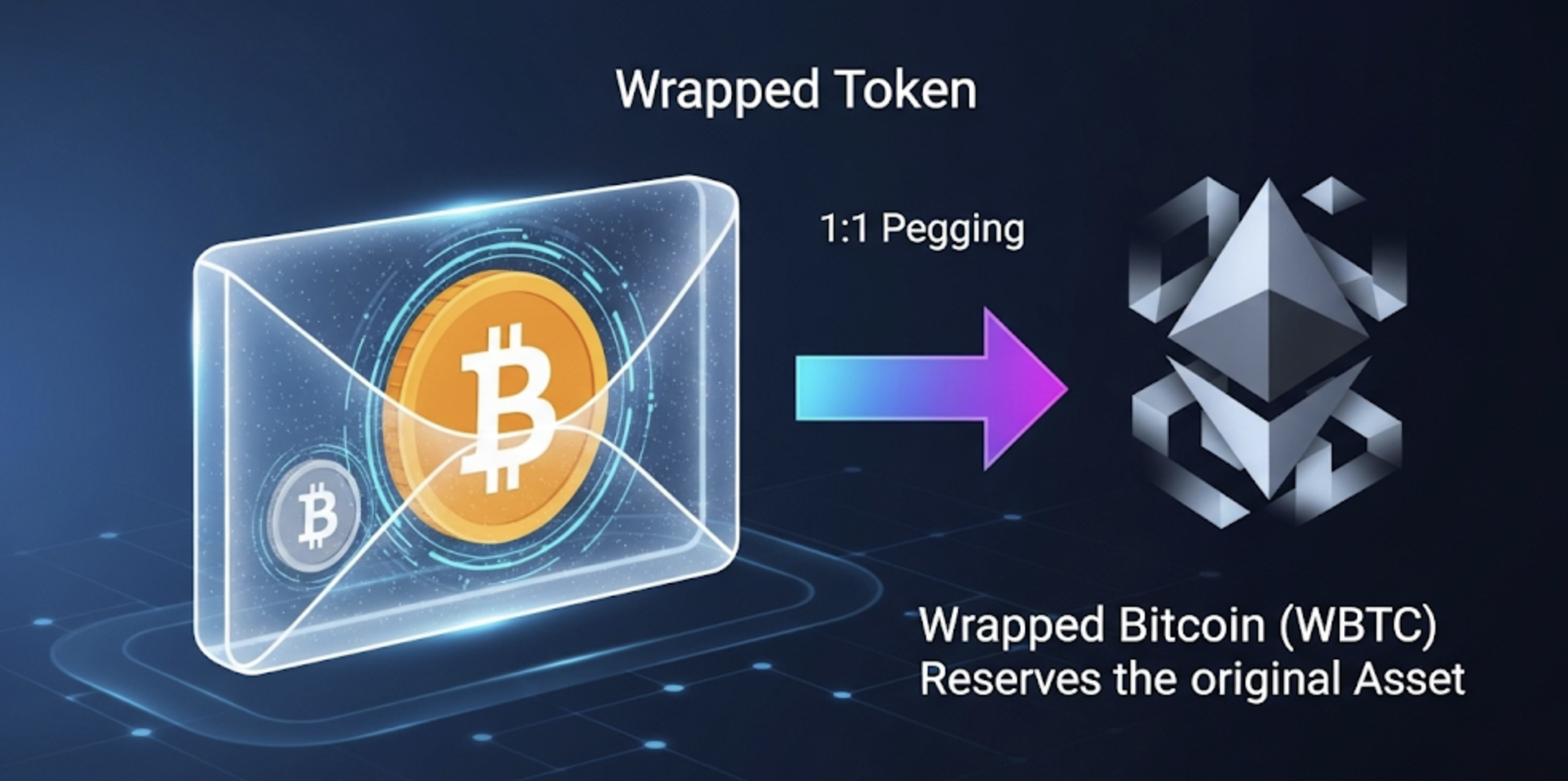
A wrapped token is a tokenized version of another cryptocurrency that can operate on a different blockchain. These tokens are pegged to the value of the asset they represent, typically at a 1:1 ratio, and can usually be redeemed at any time for the original asset.
In simple terms:
A wrapped token is a cryptocurrency “wrapped” in a digital envelope. While the real asset is securely held in reserve, its value is mirrored and used on another blockchain.
Why Do We Need Wrapped Tokens?
Cryptocurrencies operate on isolated blockchains. The Bitcoin network doesn’t know what’s happening on Ethereum. This lack of interoperability limits the broader utility of digital assets. So what if an investor holds Bitcoin but wants to participate in Ethereum-based DeFi platforms?
The solution: Wrapped Tokens.
- Want to use Bitcoin on Ethereum? → WBTC (Wrapped Bitcoin)
- Want to stake ETH on BNB Chain? → Binance-Peg ETH
- Want to buy an Ethereum NFT using BTC? → WBTC makes it possible!
How Do Wrapped Tokens Work?
The mechanism behind wrapped tokens generally works like this:
- A user sends their original asset to a trusted third party (called a custodian).
- The custodian holds the asset and mints an equivalent amount of the wrapped version on another blockchain.
- The user can use this wrapped token just like any other native token on that chain.
- When the user wants to convert back, the wrapped token is burned, and the original asset is released from the reserve.
Example: WBTC (Wrapped Bitcoin)
- A user sends BTC to the custodian.
- WBTC DAO holds the BTC in reserve.
- An equal amount of WBTC is minted on Ethereum.
- The user now has a tokenized version of Bitcoin that works in Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem.
This allows Bitcoin to be used in places where it normally couldn’t, such as Ethereum-based lending platforms or DEXs.
Wrapped Tokens vs. Stablecoins
Wrapped tokens are sometimes confused with stablecoins, as both are pegged to the value of another asset. However, they differ significantly:
| Feature | Wrapped Token | Stablecoin |
|---|---|---|
| Pegged to | Crypto asset (BTC, ETH) | Fiat currency (USD, EUR) |
| Purpose | Cross-chain utility | Price stability and spending |
| Examples | WBTC, WETH | USDT, USDC |
Benefits of Using Wrapped Tokens
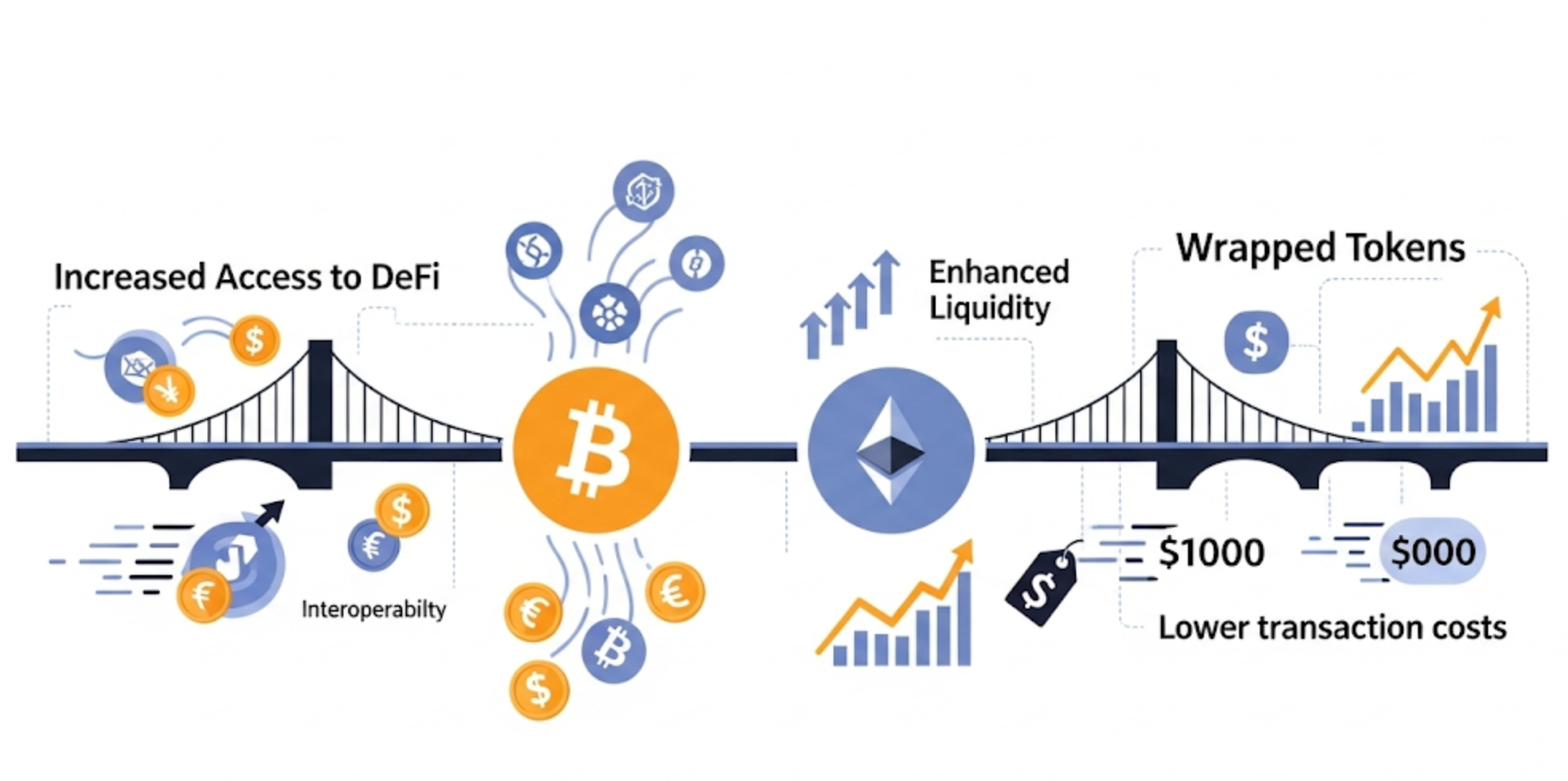
1. Bridge Between Blockchains
Wrapped tokens allow users to interact with applications across different blockchains using a single wallet.
2. Greater Access to DeFi
For example, BTC holders can participate in Ethereum DeFi platforms like Aave or Uniswap using WBTC.
3. Increased Liquidity
Wrapped tokens unlock liquidity that would otherwise remain idle, enabling greater market participation across chains.
4. Lower Transaction Costs
Bitcoin transactions can be slow and expensive. By converting BTC to WBTC, users can benefit from faster and cheaper transactions on Ethereum or Layer-2 networks.
Wrapped Token Example on Ethereum: WETH
ETH was developed before the ERC-20 token standard and thus isn’t compatible with certain smart contracts. WETH (Wrapped Ether) was created to fix this by making ETH ERC-20 compatible, allowing it to be used seamlessly in decentralized applications.
Wrapped Tokens on Binance Smart Chain: Binance-Peg Tokens
Through Binance Bridge, assets like BTC, ETH, and DOT can be converted into BEP-20 tokens for use on BNB Chain. This allows:
- Trading BTC on BSC-based DEXs.
- Earning yields with ETH on BSC DeFi platforms.
Wrapped Token Examples in the Crypto Ecosystem
| Wrapped Token | Original Asset | Host Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| WBTC | Bitcoin (BTC) | Ethereum |
| WETH | Ether (ETH) | Ethereum |
| Binance-Peg BTC | Bitcoin | BNB Chain |
| renBTC | Bitcoin | Ethereum |
| sETH | Ethereum | Synthetix |
Limitations of Wrapped Tokens
1. Centralized Custody Risk
Most wrapped tokens rely on a central entity to hold the underlying asset. If that custodian is compromised, the entire system could be at risk.
2. High Gas Fees
Wrapping and unwrapping tokens can be costly on some blockchains due to gas fees.
3. Not True Cross-Chain Transfers
Wrapped tokens don’t represent actual transfers between blockchains they are synthetic versions created to represent the asset on another network.
The Future of Wrapped Tokens
New-generation bridges like LayerZero, Axelar, and Wormhole are working to provide more decentralized, secure, and real-time wrapped token solutions. Additionally, ZK-proof-based systems are being developed to allow users to prove asset ownership without relying on centralized custodians.
Conclusion: Wrapped Tokens Make Crypto More Connected
Wrapped tokens act as bridges connecting isolated blockchains. They open up new opportunities for investors and developers alike and play a key role in expanding the utility of DeFi platforms.
In particular, large assets like Bitcoin can finally interact with decentralized ecosystems thanks to wrapped tokens. But like all technologies, users must be cautious, understand the risks, and invest wisely.
Remember: Wrapped tokens are not just a technical solution they are foundational building blocks for an interoperable, decentralized future


Comments ()