What is a Keylogger? 2025 Updated Guide

A keylogger, also known as a keystroke logger, is a software program or hardware device designed to record every keystroke made on a computer. These tools are frequently encountered in cybersecurity and can be used for both legitimate and malicious purposes. As of 2025, keylogger technologies have become more advanced, making detection and prevention increasingly complex.
What Does a Keylogger Do?
A keylogger secretly records every character typed on the keyboard without the user’s knowledge. This information can later be analyzed to obtain sensitive data such as passwords, identification numbers, and credit card details.
Keylogger Use Cases
1. Legitimate Use Cases
Keyloggers are not only used by malicious actors. In some situations, they serve legitimate purposes:
- Parental control: Used by parents to monitor their children's digital activities.
- Corporate monitoring: Employers may track employees’ computer usage during work hours. However, in countries like Turkey, this must be done with explicit consent under data protection laws.
- Research and academic studies: Utilized to study typing habits or analyze text production processes.
- Data recovery: Employed to recover unsaved typed data after system crashes.

2. Malicious Use Cases
Keyloggers are among the most favored tools for cybercriminals. Common malicious uses include:
- Stealing passwords and user credentials
- Accessing bank accounts or cryptocurrency wallets
- Intercepting private email communications
- Conducting corporate espionage
Example: If a user clicks a fake bank email and downloads malware, this software can record passwords via a keylogger.
Types of Keyloggers
Keyloggers mainly fall into two categories: hardware-based and software-based.
Hardware-Based Keylogger
- A physical device usually attached between the keyboard and the computer.
- Typically small adapters or chips.
- Some versions can be integrated into the computer’s BIOS.
- Stores data in internal memory to be retrieved later.
- Advanced models can intercept wireless keyboard signals.
Example: In an internet café, a secretly attached hardware keylogger can steal users’ account information.
Software-Based Keylogger
- The most common type.
- Installed on a computer without the user’s knowledge.
- Usually spread through phishing, malicious email attachments, or hacking software.
- Can log not only keystrokes but also screenshots, clipboard data, and mouse movements.
Common Software Types:
- API-based keylogger: Operates at the application level.
- Form grabber: Steals data entered into web forms.
- JavaScript keylogger: Uses malicious scripts running in the browser to collect data.
How to Detect and Remove Keyloggers
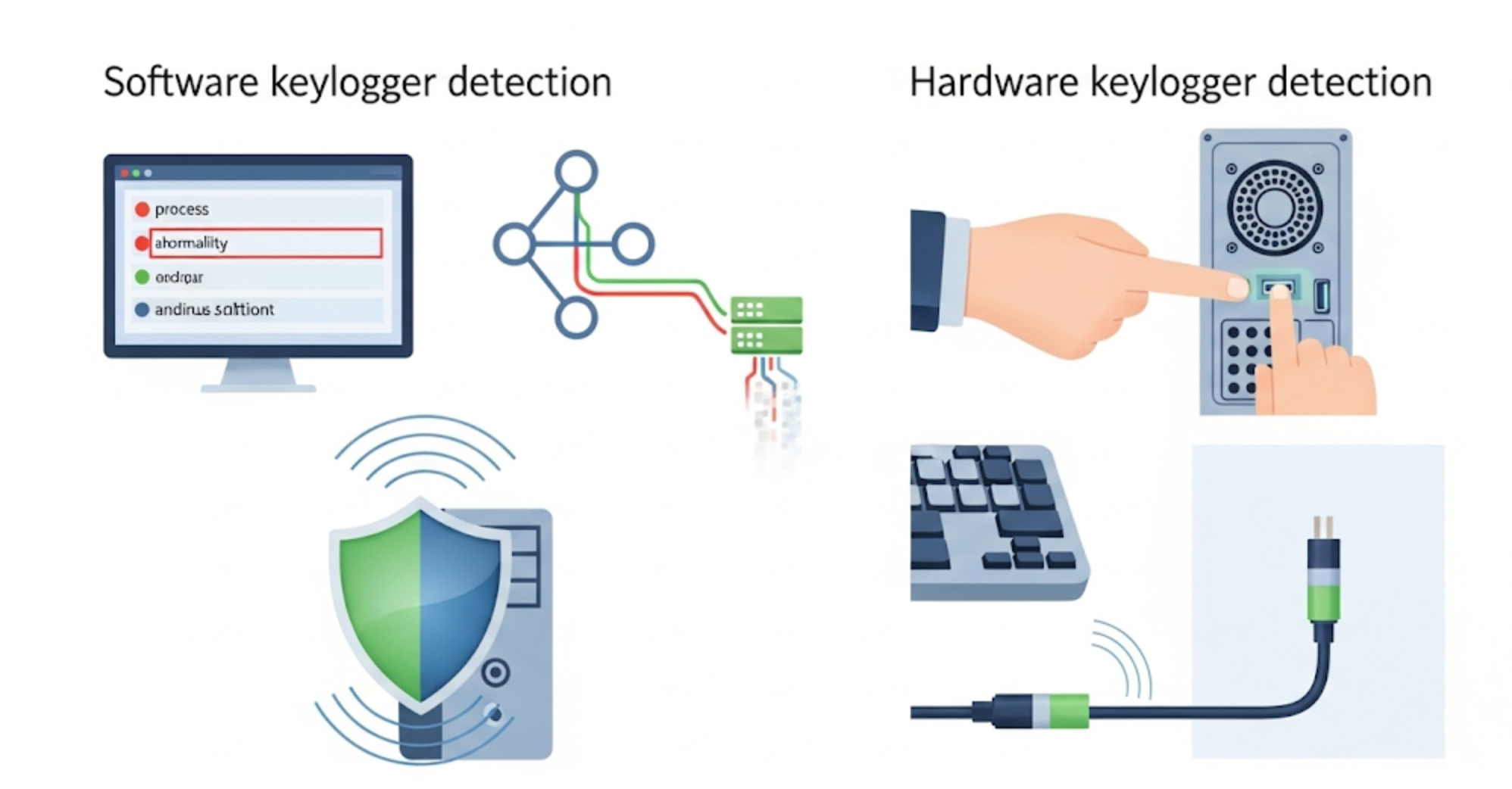
How to Detect Software Keyloggers?
- Task manager and process list: Check for suspicious running applications.
- Network traffic analysis: Examine the volume of data sent from your computer.
- Antivirus and security software: Up-to-date comprehensive security software provides significant protection.
How to Detect Hardware Keyloggers?
- Physically inspect USB or PS/2 ports on the computer.
- Look for unusual connections or additional devices on the keyboard cable.
How to Protect Yourself from Keyloggers
Protection Against Software Keyloggers
- Use updated antivirus software.
- Avoid opening email attachments from unknown sources.
- Use ad blockers and security extensions in your browser.
- Avoid installing pirated software, especially cracked files.
- Regularly update your operating system and software.
Protection Against Hardware Keyloggers
- Avoid performing sensitive transactions on public computers (libraries, hotels, internet cafes).
- Physically inspect USB connections.
- Ensure keyboard connections are not hidden or tampered with.
- Use BIOS passwords and physical security measures on personal computers.
How to Know if You Are a Victim of a Keylogger?
- Your computer runs slower than usual,
- Password changes become frequent,
- Unknown processes are running,
- There are unauthorized login attempts on your accounts,
- You notice unfamiliar software in your task manager,
These signs may indicate that your system has been infected with a keylogger.
Conclusion: Stay Informed Against Keyloggers
By 2025, cyber attacks have become more sophisticated, and keyloggers remain central to many attacks. Therefore, it is crucial for users to be aware, take security precautions, and become individuals who understand technology not just consume it.
Remember: Detecting and preventing keyloggers depends not only on software but also on user behavior. You should adopt both technical and behavioral measures to protect your security



Comments ()