What is Proof of Burn (PoB)? An Alternative Consensus Mechanism in Blockchains

Blockchain technologies use various consensus mechanisms to ensure the accuracy of transactions and secure the network. While the most commonly used methods are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), an alternative solution known as Proof of Burn (PoB) is gaining increasing attention.
In this article, we will explore in detail how the Proof of Burn mechanism works, its differences from PoW and PoS, its advantages, disadvantages, and application areas.
What is Proof of Burn (PoB)?
Proof of Burn, is an alternative consensus algorithm used in blockchains to validate transactions and create new blocks. This mechanism was first proposed by Iain Stewart and was developed especially as an energy-efficient alternative to PoW systems.
Core Concept:
Users or miners contribute to the network by sending their coins to an irretrievable address (i.e., burning them). Since these coins can no longer be used, the burning process is considered a form of investment. The more coins burned, the higher the chances of producing the next block and earning a reward.
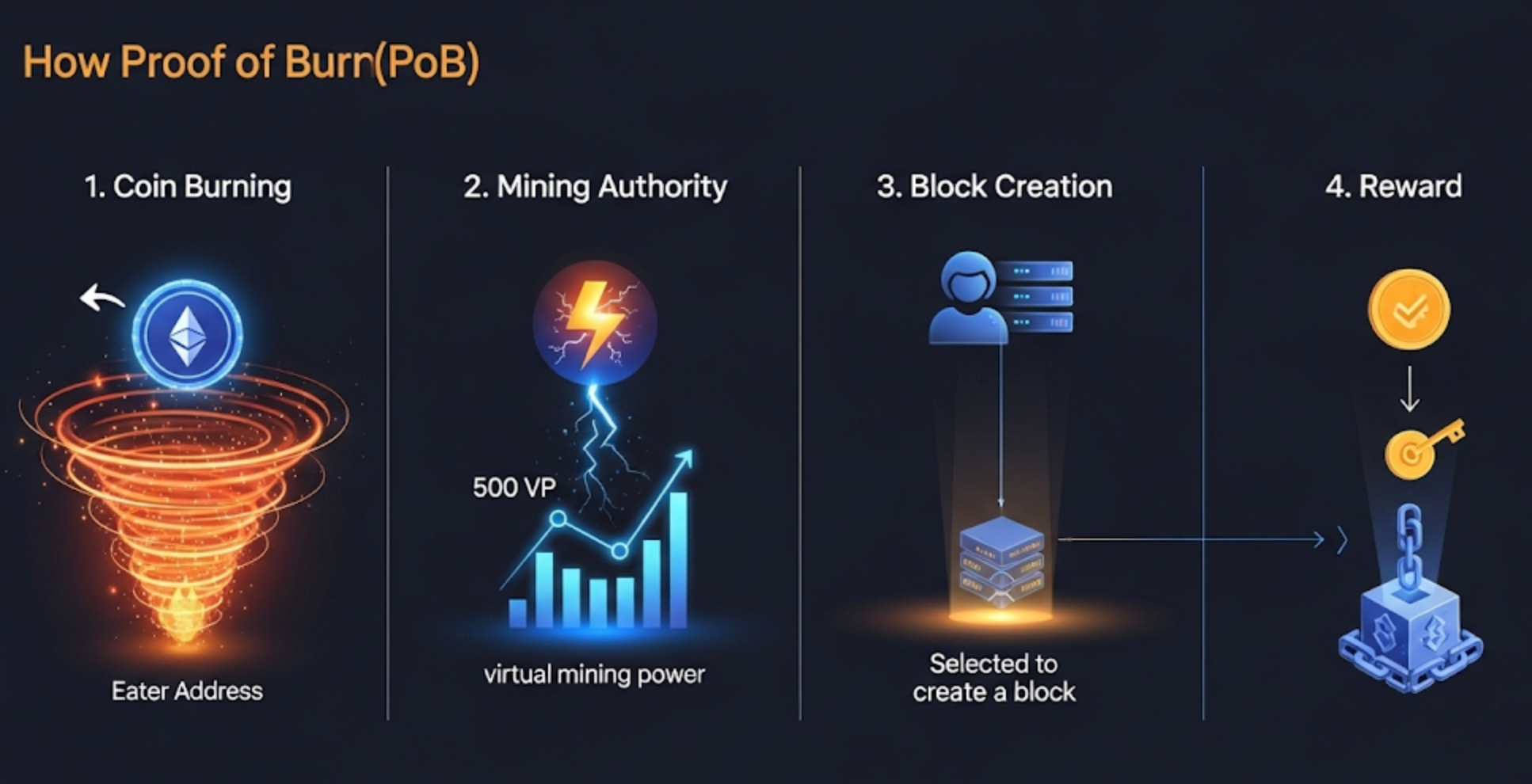
How Does Proof of Burn Work?
The working principle of the PoB algorithm consists of the following steps:
- Coin Burning: Users send their coins to "eater addresses"addresses without a private key and thus inaccessible. This transaction is permanently and publicly recorded on the blockchain.
- Mining Authority: The number of coins burned represents a user's virtual mining power. The more coins burned, the greater the mining power.
- Block Creation: Users who support the network by burning coins are granted the right to be selected as a block producer by the system.
- Reward: Users who produce new blocks are typically incentivized through transaction fees or block rewards.
Example:
In a PoB system, user A burns 100 coins, while user B burns 200 coins. In this case, user B has a higher probability of being selected to produce the next block, as they have made a greater "investment".
Comparison of Proof of Burn with Other Algorithms
PoB vs. PoW
- Energy Usage: PoB does not require high energy consumption like PoW.
- Hardware Requirement: PoB does not need ASICs or high-performance hardware.
- Mining Process: While PoW relies on physical computing power, PoB uses coin burning to generate blocks.
PoB vs. PoS
- Asset Commitment: In PoS systems, coins are temporarily locked, whereas in PoB systems, coins are permanently destroyed.
- Liquidity Impact: In PoS, staked coins can return to the market, but in PoB, burned coins are removed from circulation forever.
Advantages
- Energy Efficiency: PoB consumes significantly less energy compared to PoW.
- Hardware Independence: No need for special mining hardware.
- Supply Reduction: Coin burning permanently reduces the total supply and may lead to a potential increase in value.
- Long-Term Participation: Coin burning encourages users to commit long-term to the project.
- Decentralization: The absence of hardware barriers allows broader participation.
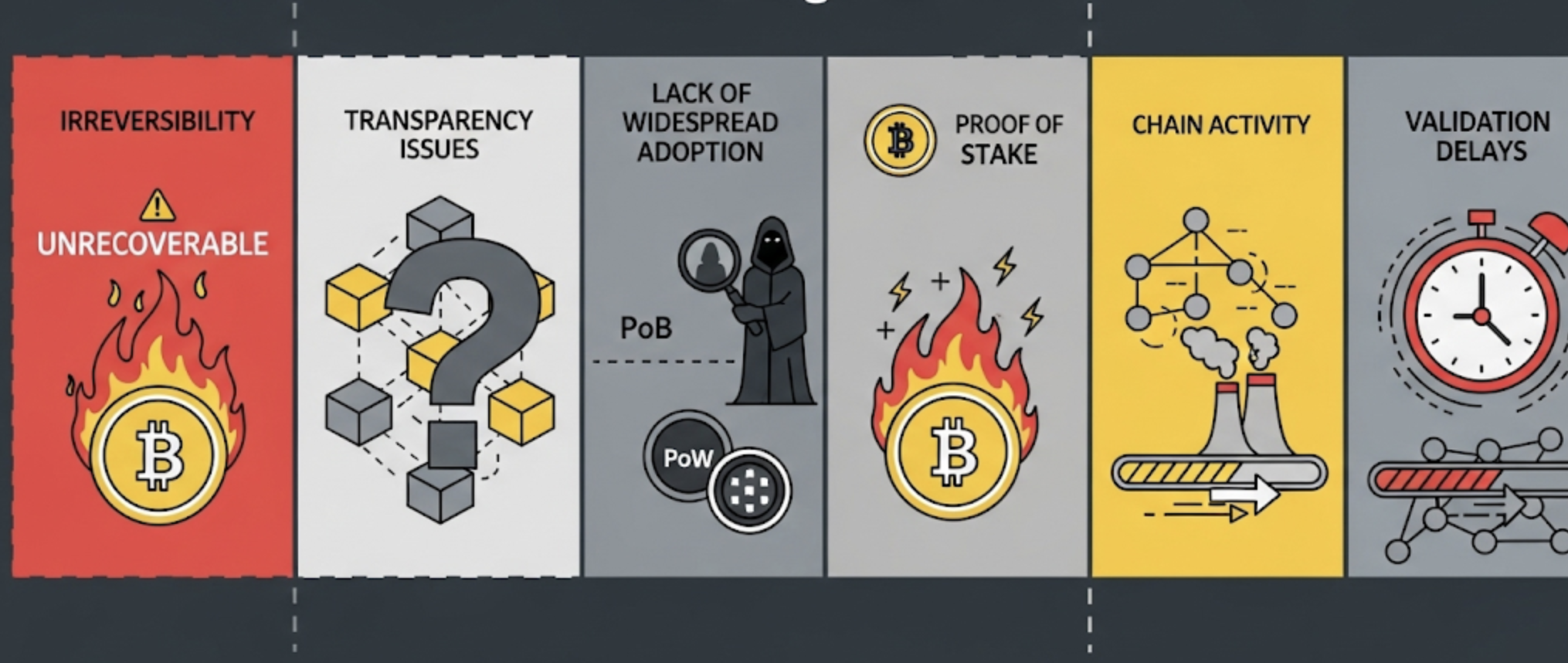
Disadvantages
- Irreversibility: Burned coins cannot be recovered, posing a risk for users.
- Transparency Issues: Burn addresses may not always be fully transparent.
- Lack of Widespread Adoption: PoB systems still have limited large-scale implementation examples.
- Chain Activity: Some of the burned coins were generated via PoW, indirectly involving energy consumption.
- Validation Delays: Block validation in PoB systems is often slower than in PoW-based systems.
Application Examples
Some projects that have tested or utilized the Proof of Burn mechanism:
- Counterparty (XCP): A platform where users can burn Bitcoin to create tokens.
- Slimcoin (SLM): Combines PoW, PoS, and PoB to offer a hybrid consensus model.
Conclusion and Evaluation
Proof of Burn is an innovative consensus algorithm designed to address issues like energy consumption. Especially its energy savings, reduction in circulating supply, and low hardware costs make it an appealing alternative.
However, the fact that PoB is not yet fully matured, not widely tested, and involves irreversible risks for users delays its broader adoption.
In Summary:
- PoB is a consensus algorithm developed to enhance sustainability in blockchains.
- It operates through coin burning as a means of block validation.
- It offers energy efficiency but involves irreversible investment risks.
- It requires more time and practical implementations to be widely accepted



Comments ()