What Mitosis Airdrop Could Be

Insights from DeFi’s Past and Airdrop Theory
Abstract
Airdrops have solidified their role as a pivotal strategy in decentralized finance (DeFi) for driving user acquisition, enhancing engagement, decentralizing governance, and expanding ecosystems.
Mitosis is a community-driven DeFi protocol and Layer-1 blockchain initiative set to launch its mainnet in July 2025, focused on building a sustainable and optimized framework for programmable ecosystem-owned liquidity (EOL).
This article conducts an in-depth examination of the potential Mitosis airdrop strategy.
Through a comparative evaluation with established DeFi protocols such as Arbitrum, Optimism, Blur, and Hyperliquid, this study integrates empirical data, theoretical frameworks, and source referencing to assess the effectiveness of various airdrop methodologies.
Findings underscore the importance of balanced tokenomics, sustained user retention strategies, and diversified engagement mechanisms in mitigating common challenges like token price depreciation and user attrition.
Mitosis’ innovative multi-channel approach, community ethos and long-term focus provides a blueprint for future DeFi projects, though its success hinges on execution and market dynamics.
I. Introduction
Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to offer permissionless financial services, reshaping traditional finance by eliminating intermediaries.
Airdrops, the distribution of free tokens to early users, have become a cornerstone of DeFi strategies to incentivize adoption, enhance platform visibility, and decentralized governance.
The September 2020 Uniswap airdrop, which distributed 400 $UNI tokens to each user and reached 250,000 wallets, set a benchmark for airdrop success by significantly boosting its user base and visibility. At the time, 400 $UNI was about $1.2K (i.e., $300M total), but by May 2021, it was worth $17K per wallet, totaling an airdrop value of $4.25B.
The electrifying hype surrounding this event propelled Uniswap to prominence, cementing its status as a leading force in the crypto industry at the time.

However, since then, many airdrops completely failed their projects and recent analyses reveal persistent challenges, with 88% of 2024 airdrops experiencing token price depreciation within 15 days. (ChainCatcher, 2024).
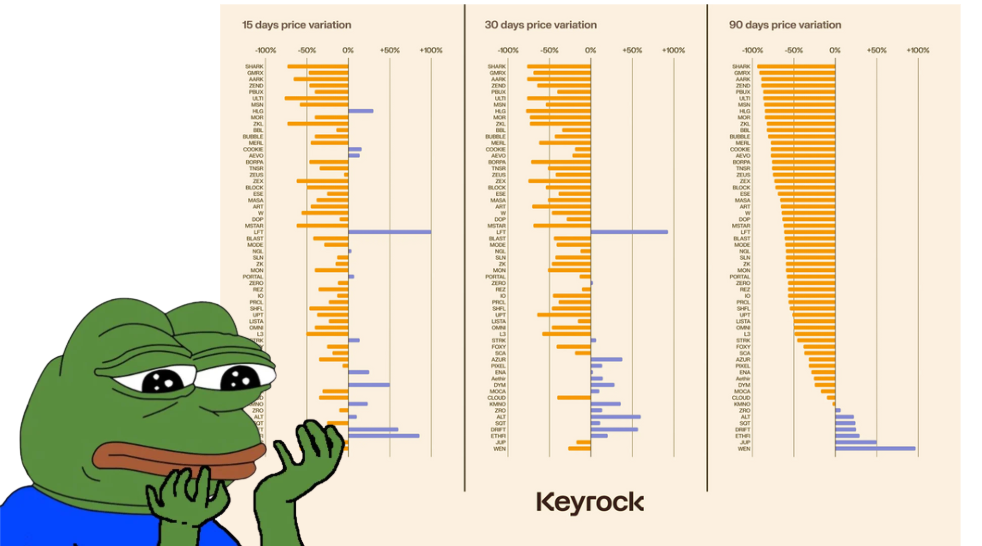
By comparing Mitosis with Arbitrum, Optimism, Blur, and Hyperliquid, this study evaluates allocation models, token price performance, user retention, and community engagement dynamics. Drawing on empirical data, theoretical frameworks, and broader market trends, this paper addresses the following research question:
How does Mitosis’ airdrop strategy could address the challenges of user retention, token price stability, and community engagement after TGE ?
II. Airdrop History: Lessons from the Past
Airdrops have evolved significantly since their inception in the cryptocurrency space. Uniswap’s 2020 airdrop, distributing thousands of dollars to 250,000 wallets, set a precedent for DeFi projects and basically a must-have.
Anyway, subsequent airdrops by Arbitrum, Optimism, Blur, and recently Hyperliquid have demonstrated varied outcomes:
Arbitrum
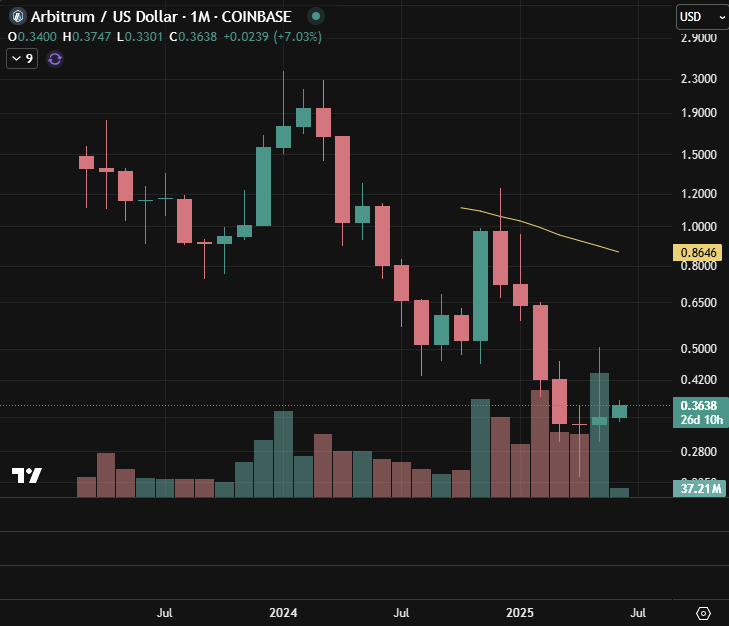
Arbitrum’s airdrop occurred on March 23, 2023, allocating 12.75% of its token supply to users to decentralize governance on its Ethereum Layer-2 network (Arbitrum Docs). The $ARB token launched at an initial price of $1.29 on that date. It peaked at $1.8 within a month but declined sharply due to selling pressure from recipients, down to $0.74. $ARB had another run at the end of 2023, along with Bitcoin and even another ATH of $2.4 in January 2024, but since then, it has declined and now sits at a modest $0.35.
In April 2025, a proposal to compensate early Arbitrum users had minimal impact on price action. Broader market pressures and Layer 2 competition were the dominant drivers. The initiative improved sentiment but not price performance.
Optimism
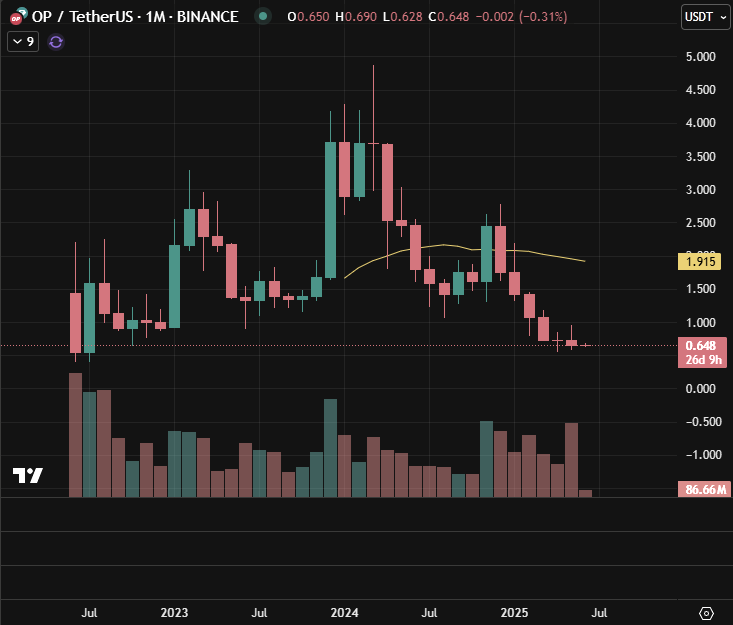
Optimism’s first airdrop was distributed on May 31, 2022, with 19% of its token supply allocated to early users to reward ecosystem contributors (Optimism Docs). The $OP token launched at $1.45 on that date.
Following the airdrop, $OP surged to a peak of $3.3 by early 2023, driven by optimism around Layer-2 adoption. However, the token faced a steady decline amid broader market corrections and post-airdrop sell-offs, dropping to $0.9 by June 2023.
Better market conditions and Optimism’s iterative airdrop strategy (including Airdrop #5 in October 2024, which distributed over 10 million $OP to Superchain users) likely contributed to renewed momentum, culminating in a new all-time high of $4.8 in March 2024. Despite these efforts, the token eventually fell sharply, trading near $0.6 by mid-2025.
Blur
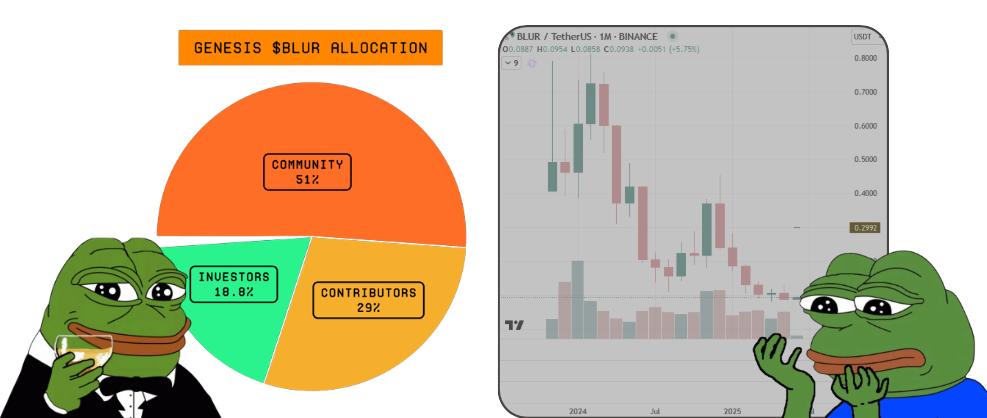
Blur, an NFT marketplace, conducted its first major airdrop on February 14, 2023, as part of a broader plan to allocate 51% of its 3 billion $BLUR token supply to the community over a 4–5 year period (Blur Foundation Docs).
The initial distribution represented 12% of the total supply and targeted early users, traders, and creators. However, the token price dropped 84% shortly after launch, from an initial $0.85 to $0.14, due to intense selling pressure.
Blur continued its incentive strategy with Airdrop Season 2 in early 2023 and Season 3 through late 2023 to May 2024, distributing hundreds of millions of tokens to boost marketplace engagement. While these campaigns temporarily elevated Blur's NFT market share (at times exceeding 70%), they also fueled concerns over wash trading and unsustainable token incentives.
As of mid-2025, $BLUR trades around $0.09, well below its launch price.
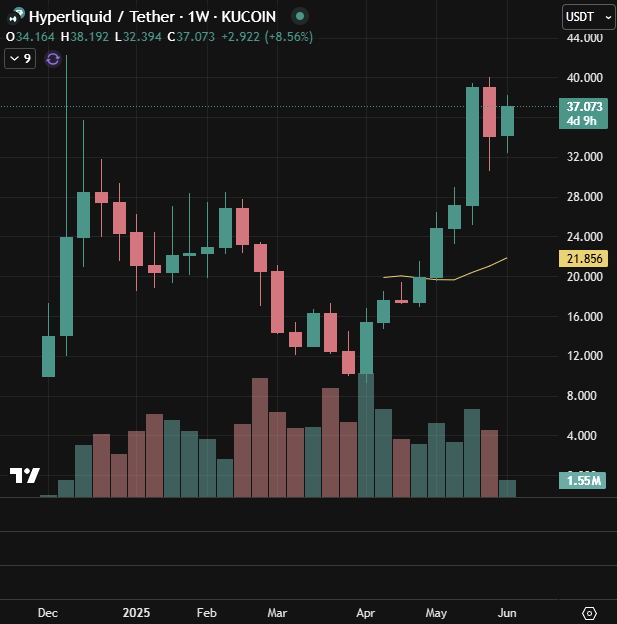
Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid, a high-performance Layer 1 chain focused on decentralized perpetual futures, launched its native token $HYPE on November 29, 2024, via a major airdrop. Roughly 31% of the total 1 billion $HYPE supply was distributed to over 90,000 users, primarily active traders and early supporters (Hyperliquid Docs). The initial airdrop had a decisively bullish impact on price action.
Unlike other protocols that suffered from post-airdrop sell-offs, $HYPE gained value in the weeks following its launch. Analysts attribute this resilience to several factors:
- No VC Unlock Pressure: Hyperliquid has no external funding or token allocations to venture capital firms, removing the common overhang of early investor sell pressure.
- High Platform Stickiness: A large portion of the airdropped tokens was quickly staked: over $1 billion in HYPE was locked, indicating a strong conviction among recipients.
- Sustained Trading Volume: Hyperliquid accounted for over 80% of on-chain perp trading activity in May 2025, suggesting deep utility for the token within its ecosystem.
These dynamics helped propel $HYPE to an all-time high of $39.89 by June 2025, a rare post-airdrop success story in DeFi.
Ongoing initiatives, including staking rewards, loyalty incentives, and prospective future airdrops, continue to drive demand and lock-in behavior.
With 38.9% of the supply still reserved for long-term community rewards, further price support may come from user retention strategies rather than speculative hype alone.
Lessons Learned
Airdrops have evolved from one-time giveaways into strategic tools for ecosystem growth, but their impact on token price and sustainability varies widely.
Arbitrum, Optimism, and Blur all saw initial hype followed by sharp declines, highlighting the risks of large token distributions without sufficient lockups or lasting utility.
In contrast, Hyperliquid’s HYPE token broke the pattern: its airdrop fueled sustained growth thanks to strong product traction, no VC sell pressure, and high staking engagement. This shows that when well-designed, airdrops can be more than marketing: they can drive long-term value if aligned with real user demand and protocol incentives.
III. Theoretical Tools for Smarter Airdrop Design
Why Theory Matters
The empirical lessons from past airdrops underscore three recurring challenges: (1) rapid token depreciation,
(2) user attrition after initial engagement, and
(3) weak community integration.
To structure a framework for understanding how these issues might be mitigated, we turn to three academic lenses:



- Coevolutionary Design (Allen et al., 2023):
This theory suggests that blockchain protocols and their user communities engage in a dynamic, adaptive process, each responding to changes in the other. In the context of airdrops, protocols that evolve eligibility requirements, reward schemes, or engagement mechanics based on user behavior tend to achieve more resilient ecosystems.
Allen et al. demonstrate that iterative feedback and adaptive allocation strategies outperform static airdrops, which are often exploited and forgotten. The coevolutionary model implies that optimal airdrop design is not a one-time event but an ongoing refinement aligned with observed participation patterns. - Behavioral Incentive Structures (Yaish & Livshits, 2024):
In their TierDrop model, the authors argue that airdrop farmers (users who engage solely for token rewards) should not necessarily be excluded. Instead, protocols should design incentive tiers that harness this group’s economic behavior in a way that contributes to growth.
By modeling platform competition, the authors find that optimal outcomes occur when farmers are strategically included and gradually incentivized toward deeper engagement.
This approach draws on behavioral economics principles, recognizing that users respond to token rewards in ways that can either hollow out or strengthen network participation depending on design. - Network Growth Modeling (Makridis et al., 2021):
This framework emphasizes how airdrops can be tools to accelerate network effects.
Makridis et al. demonstrate that successful airdrops act as seeding mechanisms for network expansion, i.e. when they tie recipients into long-term use cases such as staking, governance, or liquidity provision.
The key insight is that token distribution must create 'embeddedness' within the protocol: users must find recurring reasons to interact with the platform. Without this, user drop-off is highly probable.
These frameworks offer complementary insights for evaluating the Mitosis airdrop strategy.
IV. What Could Be the Mitosis Airdrop
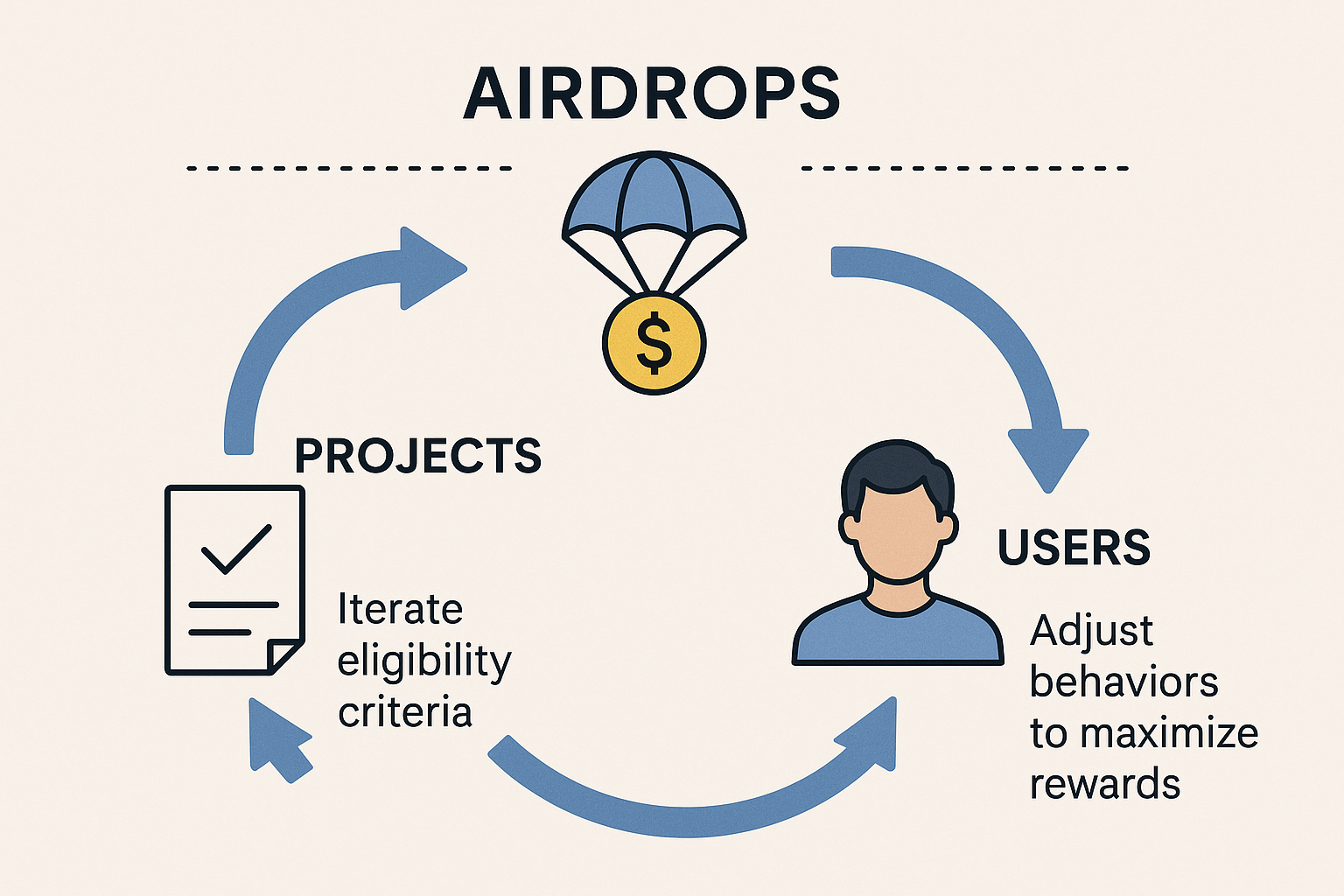
1. Airdrops as Coevolutionary Systems
Airdrops are adaptive mechanisms, not static events. Projects and users co-evolve: users adjust behaviors to maximize airdrop rewards, while protocols must iterate eligibility criteria to align user incentives with long-term goals.
Hyperliquid Success: Introduced staking immediately, bypassed VC sell pressure, and reinforced usage-based rewards.
Failure Cases: Blur incentivized short-term engagement; Arbitrum and Optimism lacked follow-up mechanisms post-distribution.
Mitosis Application: Already reflects coevolutionary traits: Community-driven, feedback adjustments (e.g., Yapper criteria), multi-stage eligibility systems (Expedition, testnet, Discord roles) and DAO governance alignment (DNA program).
Recommendations: Implement multi-round airdrops tied to user behavior; evolve criteria transparently; enable post-launch adaptive learning via DAO discussions and decisions.
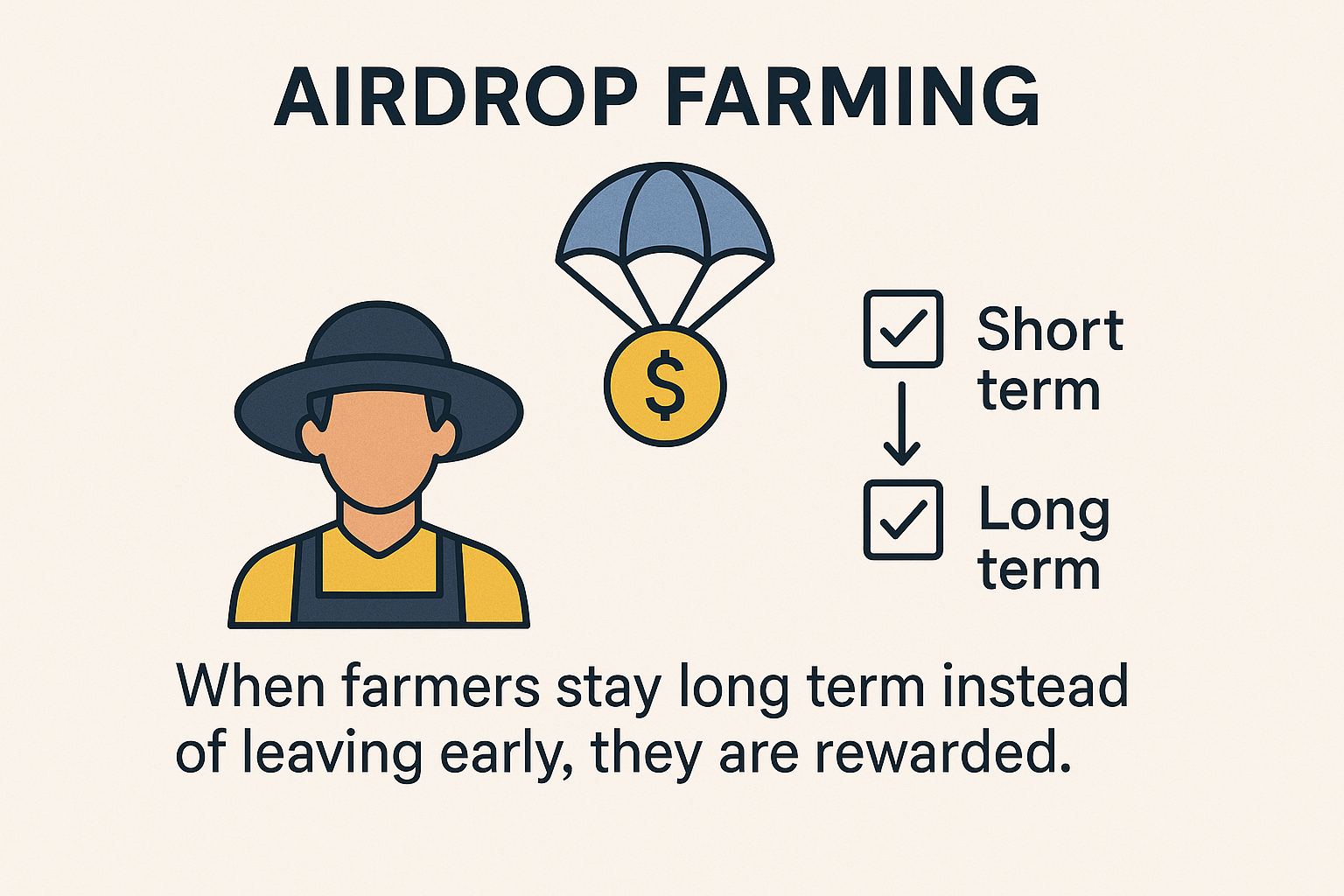
2. Incentive Engineering and Behavioral Adaptation
Airdrop farming is not inherently negative and can be utilized as part of a growth strategy. Instead of designing mechanisms to exclude farmers, projects should embed them in a structured system that rewards long-term contributions.
Hyperliquid Success: High token lock-in and sticky user behavior demonstrated that incentives aligned with user motivations can sustain engagement.
Failure Cases: Blur and Arbitrum attracted extractive behaviors due to front-loaded, unstructured rewards.
Mitosis Application: The multi-tiered Expedition Campaign with scaling multipliers and engagement via NFTs and social roles help transitioning from opportunistic users to more embedded contributors through recurring eligibility conditions and evolving reward structures.
Recommendations: Expand tier structures across future campaigns, ensure recurring participation milestones, and incentivize long-term behavioral patterns.
If executed properly, DNA program announced recently with reward structure linked to locking tokens should also increase user retention rate.
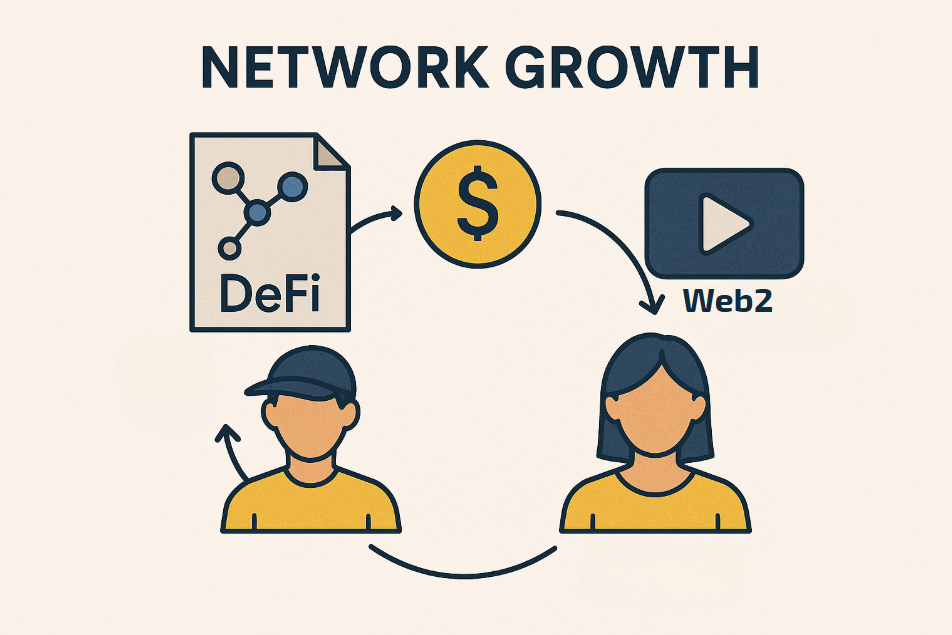
3. Network Growth and Embedded Communities
Airdrops succeed when recipients become stakeholders, not exit-seeking traders. Strong protocols embed tokens in community and utility networks.
Hyperliquid Success: Trading volume created organic token demand. No KOL favoritism. Airdrop recipients were also core users.
Failure Cases: Blur suffered wash trading. Arbitrum and Optimism had passive recipients.
Mitosis Application: The main attraction should be EOL efficiency. Existing users will stay, and new users will join if they find no better alternatives elsewhere. Strong connections with NFT (and other) communities will sustain broader crypto engagement.
Partnerships with mainstream-focused blockchains or dApps could further boost participation and offset the departure of hardcore DeFi farmers. (PetrAnto Mitosis University, 2025).
Recommendations: Strengthen token utility in governance and liquidity; reinforce community bonds via cohort-based rewards; user acquisition as a strong focus.
V. Conclusion
This analysis demonstrates that effective airdrop strategies must do more than simply distribute tokens: they must strategically engineer participation, reward mechanisms, and community alignment to create sustained network effects.
The failures of Arbitrum, Optimism, and Blur reveal that token price volatility and user attrition are not just market outcomes but design issues.
In contrast, Hyperliquid’s success shows that embedding user incentives, eliminating extractive participants, and aligning airdrops with actual protocol usage can lead to post-airdrop growth.
Mitosis shows promising potential by applying several of these principles through its Expedition Campaign, EOL integration, and multi-tiered engagement architecture.
However, realizing this potential will require continued iteration, transparent eligibility evolution, and a careful balance between inclusivity and commitment. Airdrops are no longer about distribution: they are about network construction, and Mitosis is positioned to lead if it manages to use its airdrop as an investment towards its DAO community.


Comments ()